The full form of DRS in cricket is Decision Review System. It is a technology-based system used to help umpires make correct decisions. Players can challenge an umpire’s call if they think it is wrong. The third umpire then uses special tools like ball tracking and UltraEdge to review the decision. DRS makes the game fairer by reducing human errors and improving accuracy in umpiring.
DRS Full Form in Cricket
Cricket is a sport that has seen numerous technological advancements over the years. One such innovation that has had a profound impact on the game is the Decision Review System, commonly known as DRS. DRS is a comprehensive tool that helps in making more accurate decisions on the field, thereby reducing the margin for error in critical moments. In this article, we will explore the full form and function of DRS in cricket and its impact on the sport.
What is DRS?
DRS stands for Decision Review System. It is a technology-driven system that was introduced to assist the on-field umpires in making crucial decisions during a cricket match. The primary objective of DRS is to reduce errors and ensure that decisions related to dismissals and various other aspects of the game are as accurate as possible.
Components of DRS
The Decision Review System comprises several key components:
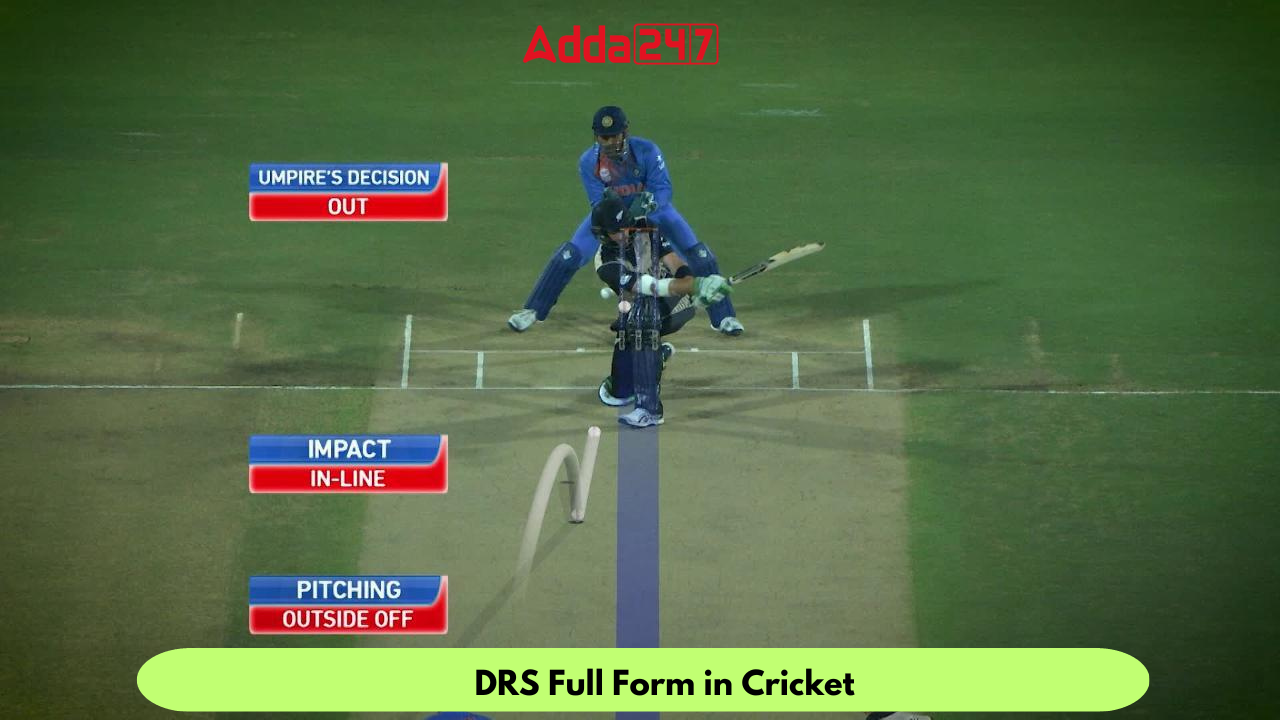
Ball Tracking Technology: This component uses multiple cameras to track the path of the ball from the bowler’s hand to the point of impact with the batsman. It helps determine the trajectory, swing, and spin of the ball, aiding in decisions related to LBW (Leg Before Wicket) and caught-behind dismissals.
Hot Spot: Hot Spot technology employs infrared cameras to detect temperature variations on the bat or the pad. This is particularly helpful in assessing edges and the impact of the ball on the batsman’s body or equipment.
Snickometer: The Snickometer, also known as Ultra Edge, uses sound sensors to detect small sounds when the ball touches the bat or pad. It is particularly useful for identifying faint edges.
Hawk-Eye: Hawk-Eye is a ball-tracking system that predicts the trajectory of the ball and its potential impact on the stumps. It helps in LBW decisions and provides a visual representation of the ball’s path.
Umpire’s Call: Umpire’s Call is an important aspect of DRS. It allows the on-field umpire’s decision to stand if the technology indicates that the decision is within a certain margin of error.
How DRS Works?
When a team decides to review an umpire’s decision, they signal to the third umpire, who has access to all the DRS technology. The third umpire reviews the available footage and technology data to make a more accurate assessment of the decision. If there is conclusive evidence to overturn the on-field decision, it is changed. If not, the on-field decision stands.
Impact of DRS on Cricket
Fair Play: DRS has made the game fairer by reducing human errors. It ensures that players are not unfairly dismissed or not given out when they should be.
Dramatic Moments: The technology has added an extra layer of drama to the game, with teams and players using their limited DRS reviews strategically. The tension and excitement of DRS reviews have become an integral part of modern cricket.
Educational Tool: DRS technology has also been beneficial for players and spectators. It provides insights into the intricacies of the game, helping fans and players understand the nuances of ball movement and impact.
Challenges and Controversies: While DRS has been largely beneficial, it hasn’t been without its share of controversies. The accuracy of the technology, the use of ball-tracking in LBW decisions, and the discretion of the third umpire have been subjects of debate.
In conclusion, the Decision Review System (DRS) has had a profound impact on the game of cricket. It has increased the accuracy of decisions, added drama to matches, and educated fans and players alike. While it may not be without its challenges, DRS remains an essential tool in modern cricket, ensuring the spirit of the game is upheld while striving for greater accuracy in decision-making


 Cricketers Javon Searles, Griffith and R...
Cricketers Javon Searles, Griffith and R...
 India Women's Hockey Qualified For Hocke...
India Women's Hockey Qualified For Hocke...
 Shailesh Kumar Wins Gold at World Para A...
Shailesh Kumar Wins Gold at World Para A...








