The 2024 Global Water Monitor Report highlights significant disruptions in the global water cycle due to climate change, which led to devastating water-related disasters worldwide. These events caused over 8,700 deaths, displaced 40 million people, and resulted in economic losses exceeding $550 billion. The report emphasizes how extreme weather events, such as landslides, floods, and droughts, are becoming more frequent and intense due to global warming, affecting ecosystems, livelihoods, and infrastructure. Among the major events highlighted, the Wayanad landslides in India stood out as a particularly destructive disaster.
Key Points from the 2024 Report
Global Water Cycle Disruption
- Climate change significantly altered the global water cycle in 2024.
- The disruption contributed to water-related disasters like landslides, floods, droughts, and tropical cyclones.
- Over 8,700 deaths, 40 million displaced, and $550 billion in economic losses.
Wayanad Landslides (India)
- Triggered by 409mm of rainfall in 24 hours in July 2024.
- 375 lives lost and 10,000 displaced.
- Economic losses of $140 million.
- Highlighted as a key example of the deadly impacts of climate-induced rainfall events.
Other Major Disasters
- Flash floods and river floods in Afghanistan, Pakistan, and East Africa.
- Severe flooding in Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil) and heavy flooding in the Amazon Basin (Brazil).
- Tropical cyclones, landslides, and droughts attributed to rising global temperatures.
Climate Change Impact
- Rising sea surface temperatures contributed to prolonged droughts in Southern Africa and the Amazon.
- Extreme rainfall events occurred 52% more frequently in 2024 compared to previous decades.
- Record-dry months increased by 38%, intensifying water scarcity.
Temperature and Precipitation Trends
- 2024 recorded the highest-ever average global land temperatures.
- A significant rise in extreme rainfall and extreme dry months.
- 34 countries experienced record-high annual maximum temperatures.
- The frequency of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and flash floods, increased.
Declining Water Storage
- Global reductions in lake and reservoir water storage for the fifth consecutive year.
- Declines were particularly significant in South America, while increases were seen in certain regions of Africa.
Forecast for 2025
- Potential for more extreme weather events, including flash floods, droughts, intense storms, and heatwaves.
- Regions at risk: Northern South America, Southern Africa, Central Asia, North America, and Western Australia.
- Increased flooding risks in Sahel, Horn of Africa, Europe, and Asia.
| Summary/Static | Details |
| Why in the news? | Global Water Cycle Disruption in 2024 Caused Wayanad Landslides |
| Water-related Disasters | 8,700 deaths, 40 million displaced, $550 billion in economic losses due to extreme weather events like floods, droughts, and landslides. |
| Wayanad Landslides | 409mm rainfall in 24 hours in July 2024, 375 deaths, 10,000 displaced, $140 million in damages. |
| Other Major Disasters | Flash floods in Afghanistan, Pakistan, East Africa; floods in Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil); Amazon drought and bushfires. |
| Climate Change Impact | Sea surface temperatures, extreme rainfall, and rising temperatures intensifying water-related disasters. |
| Temperature & Precipitation | Highest-ever average land temperatures, 52% increase in extreme rainfall events, 38% more record-dry months. |
| Water Storage Decline | Continued decline in lake and reservoir storage for five consecutive years; reduction in South America, increases in parts of Africa. |
| 2025 Forecast |
Increased risks of flash floods, droughts, storms, and heatwaves, especially in Northern South America, Southern Africa, and Central Asia.
|



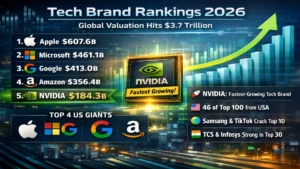 Top 10 Most Valuable Technology Brands i...
Top 10 Most Valuable Technology Brands i...
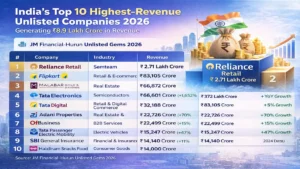 Top 10 highest-revenue unlisted Indian c...
Top 10 highest-revenue unlisted Indian c...
 India’s Top 10 Richest and Poorest State...
India’s Top 10 Richest and Poorest State...








