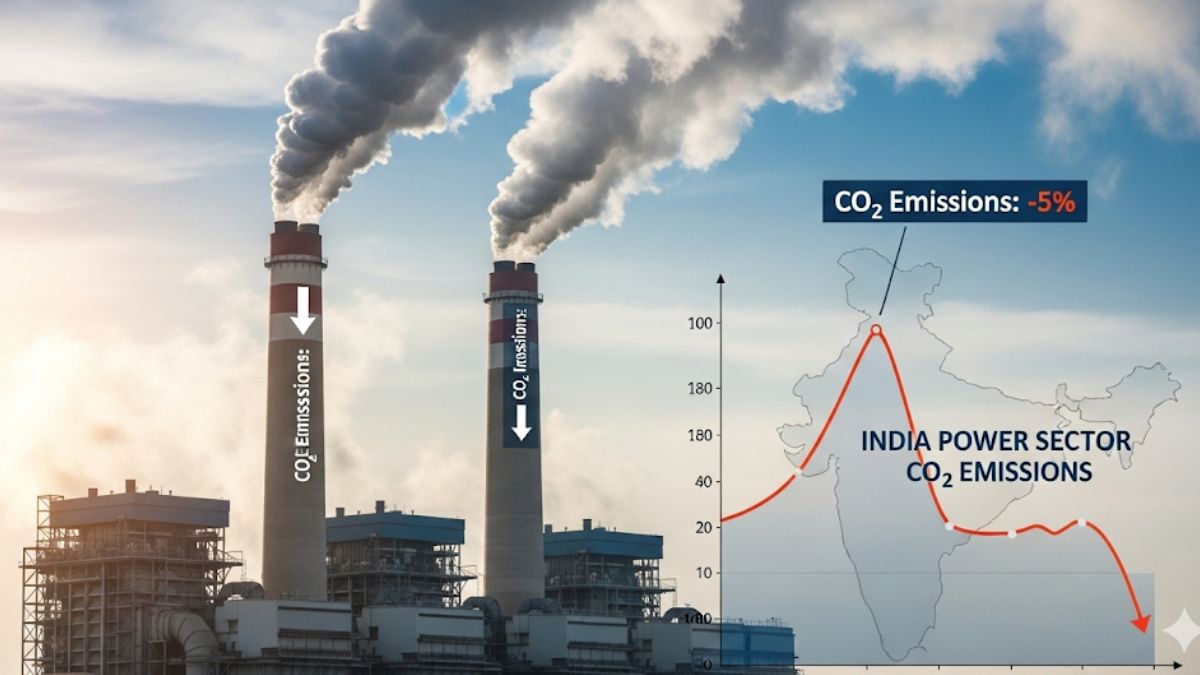
For the first time outside a crisis period like the COVID-19 lockdown, India has recorded a fall in carbon dioxide emissions from its electricity sector. According to an analysis by the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) for the UK-based Carbon Brief, CO₂ emissions dropped by 1% between January and June 2025, compared to the same period in 2024.
Given that the electricity sector accounts for nearly 40% of India’s total greenhouse gas emissions, this minor but symbolic decline is a landmark development in the country’s environmental trajectory.
What Caused the Emission Drop?
The analysis identifies two major reasons behind the decline,
1. Structural Growth in Clean Energy
- India added 25.1 GW of clean energy capacity in the first half of 2025—a 70% jump over last year.
- These additions included solar, wind, hydropower, and nuclear installations.
- As a result, fossil fuel-based generation fell by 29 terawatt-hours, despite an overall increase in electricity production.
2. Reduced Electricity Demand
- A milder summer and good pre-monsoon rainfall significantly reduced the use of air conditioning, which typically contributes up to 10% of peak electricity demand.
- This led to lower coal consumption, especially during high-demand periods.
India’s Emission Profile: Context and Targets
- India is currently the third-largest CO₂ emitter in the world, behind China and the US.
- Historically, its emissions have risen steadily with economic growth.
- The government has set a national target of 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- As of mid-2025, 252 GW has already been achieved.
- An additional 230 GW is in the project pipeline, potentially pushing the total to 482 GW before 2030.
Statement by Officials
Union Minister for New and Renewable Energy, Prahlad Joshi, stated that,
- India installed 23 GW of clean energy capacity in just five months (April–August 2025).
- The remaining months are expected to double this figure.
- This shows that renewable energy deployment is accelerating, possibly peaking India’s power sector emissions before 2030, far earlier than previously projected.
Static Facts
- Emission Drop: 1% decline in electricity sector CO₂ emissions (H1 2025 vs H1 2024)
- Key Reason: Clean energy growth + mild summer
- Clean Energy Added (H1 2025): 25.1 GW
- Total Non-Fossil Capacity Achieved: 252 GW (as of 2025)
- National Target: 500 GW by 2030


 Govt Launches Mobile Labs to Check Natio...
Govt Launches Mobile Labs to Check Natio...
 Big Change at Rashtrapati Bhavan! Lutyen...
Big Change at Rashtrapati Bhavan! Lutyen...
 India Launches ‘Prahaar’: New National C...
India Launches ‘Prahaar’: New National C...








