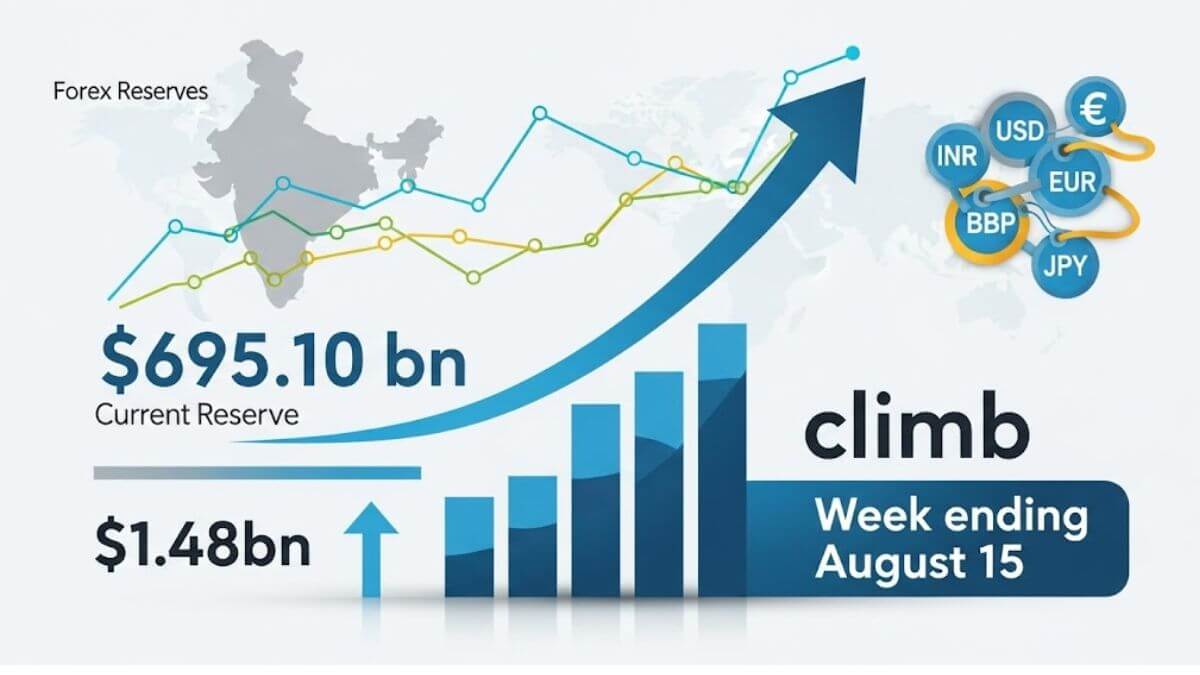
India’s foreign exchange reserves continued their upward trajectory, increasing by $1.48 billion to $695.10 billion for the week ending August 15, 2025, as per the latest data released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). This rise, driven largely by higher foreign currency assets, comes after a period of volatility in global markets and underscores the central bank’s active role in ensuring currency stability.
Breakdown of the Reserve Components
The total reserves, which serve as a key buffer against external shocks, comprise several components,
- Foreign currency assets (FCA) rose significantly by $1.92 billion, reaching $585.90 billion. These assets include investments in major global currencies like the euro, yen, and pound, which are held in non-US denominations but converted into dollar terms for reporting. The FCA is sensitive to exchange rate fluctuations and valuation changes.
- Gold reserves, in contrast, declined by $2.16 billion, bringing the total value down to $86.16 billion. This decrease could reflect a dip in global gold prices or portfolio rebalancing by the RBI.
- India’s reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) increased modestly by $15 million, standing at $4.75 billion.
Context: All-Time High and Recent Trends
India’s forex reserves had touched an all-time high of $704.885 billion in September 2024. Although the current level is slightly below that peak, the ongoing accumulation highlights India’s comfortable external sector position amid global uncertainties.
Earlier in August 2025, reserves had declined for three consecutive weeks. The current recovery indicates renewed capital inflows or valuation gains from currency holdings.
RBI’s Role in Forex Market Stability
The Reserve Bank of India plays a pivotal role in managing the foreign exchange market. While it does not target a specific exchange rate, the RBI intervenes when needed to,
- Prevent excessive rupee depreciation or appreciation.
- Ensure orderly market conditions by limiting high volatility.
- Use tools like selling or buying dollars to regulate liquidity.
- This approach maintains investor confidence and shields the economy from abrupt capital flight or currency mismatches.


 India Revises Base Year of Merchandise T...
India Revises Base Year of Merchandise T...
 India’s Core Sector Growth Slows to 4% i...
India’s Core Sector Growth Slows to 4% i...
 Unemployment Rises to 5%! Why India’s Jo...
Unemployment Rises to 5%! Why India’s Jo...








