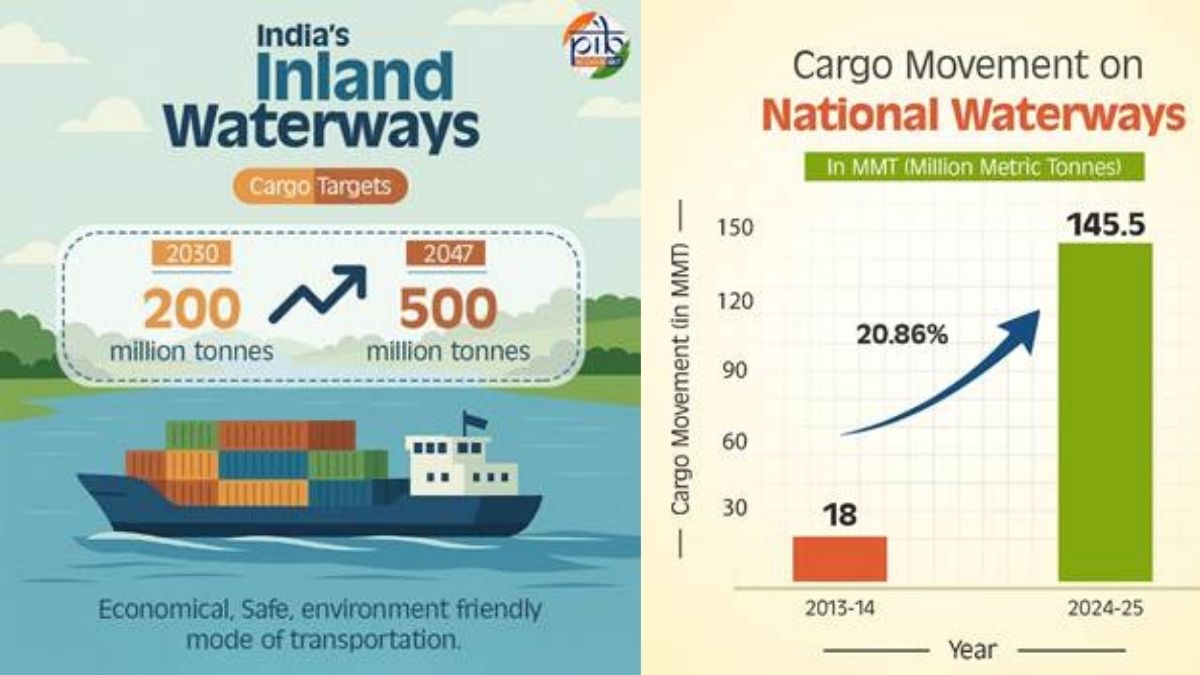
India has achieved a significant milestone in its inland water transport (IWT) sector by recording 145.5 million tonnes (MMT) of cargo movement during the fiscal year 2024–25. This marks a dramatic rise from just 18.1 MMT in FY 2013–14, driven by massive infrastructure development, policy reforms, and technological innovations. The country has also expanded its National Waterways from 5 to 111 and increased the operational length to nearly 4,900 km, reflecting a strong commitment to multimodal logistics and sustainable development.
Key Highlights and Developments
Record Cargo Traffic
- 145.5 MMT cargo moved in FY 2024–25, up from 18.1 MMT in FY 2013–14
- CAGR of 20.86% over the last decade
- 9.34% YoY growth from FY 2023–24
- Top 5 commodities: Coal, Iron Ore, Iron Ore Fines, Sand, and Fly Ash (68% of total cargo)
Expansion of National Waterways
- NWs increased from 5 (2014) to 111 (under NW Act, 2016)
- Operational length grew from 2,716 km to 4,894 km
- 29 National Waterways currently operational
Infrastructure Development
- Multi-Modal Terminals (MMTs), Inter-Modal Terminals (IMTs), floating and community jetties
- Advanced fairway maintenance and navigational support
- Examples: MMTs at Varanasi, Haldia, Pandu, Jogighopa; terminals at Dhubri, Bogibeel
- Digital and Green Technologies
- Tools like LADIS, RIS, PANI, MIRS to boost operational efficiency
- Adoption of green vessels: Hybrid Electric Catamarans, Hydrogen-fueled boats
Passenger Movement
- 1.61 crore passenger movement recorded in 2023–24
Policy Measures to Boost IWT
Jalvahak Scheme
- Launched in Dec 2024; ₹95.42 crore outlay
- 35% reimbursement on operating cost for shifting cargo to waterways
- Scheduled services on key routes (NW-1, NW-2, NW-16)
Tonnage Tax Extension
- Extended to inland vessels from Feb 2025
- Taxation based on tonnage, not profit — more predictable and lower tax burden
Regulatory Framework for Private Investment
- New regulations notified in 2025 for private jetties/terminals
Port Integration
- MMTs and IMTs transferred to Shyama Prasad Mookerjee Port, Kolkata
Digitisation
- Centralised vessel and crew registration portal (like Vahan/Sarathi)
Cargo Aggregation Hubs
- Freight Village at Varanasi
- Integrated Cluster-cum-Logistics Park at Sahibganj
Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route
- Trial on Routes 5 & 6 between Maia and Sultanganj successful
PSU Engagement
- Over 140 PSUs engaged to shift cargo to IWT
- Ministries like Petroleum, Coal, Fertiliser, Steel involved
| Summary/Static | Details |
| Why in the news? | India’s Record Cargo Movement on Inland Waterways In FY 2024–25 |
| Record Cargo Movement | 145.5 MMT in FY 2024–25 (CAGR: 20.86%) |
| National Waterways | Increased from 5 (2014) to 111 (2024) |
| Operational NW Length | 4,894 km (up from 2,716 km in 2014–15) |
| Passenger Movement | 1.61 crore in 2023–24 |
| Key Commodities | Coal, Iron Ore, Sand, Fly Ash (68% of cargo) |
| Major Projects | MMTs, IMTs, community jetties, fairway maintenance |
| Green Technology | Hybrid Electric, Hydrogen vessels introduced |
| Jalvahak Scheme | ₹95.42 crore; 35% cost incentive |
| Tonnage Tax | Extended to inland vessels (Feb 2025) |
| Digital Tools | LADIS, RIS, PANI, MIRS, centralised registration |
| Indo-Bangladesh Route | Routes 5 & 6 trialled successfully |



 ICRA Projects India’s GDP Growth to Mode...
ICRA Projects India’s GDP Growth to Mode...
 India’s GDP May Hit 8.1% in Q3FY26: SBI ...
India’s GDP May Hit 8.1% in Q3FY26: SBI ...
 Forex Reserves of India Hit Record High ...
Forex Reserves of India Hit Record High ...








