The invention of the diesel engine dates back to the 1890s. Since then, diesel engines have become one of the most common engines used in power generation and various industries. Diesel generator technicians or mechanics work on these powerful engines and generator systems, setting up and maintaining them to meet customer specifications.
Early Development and Invention of the Diesel Engine
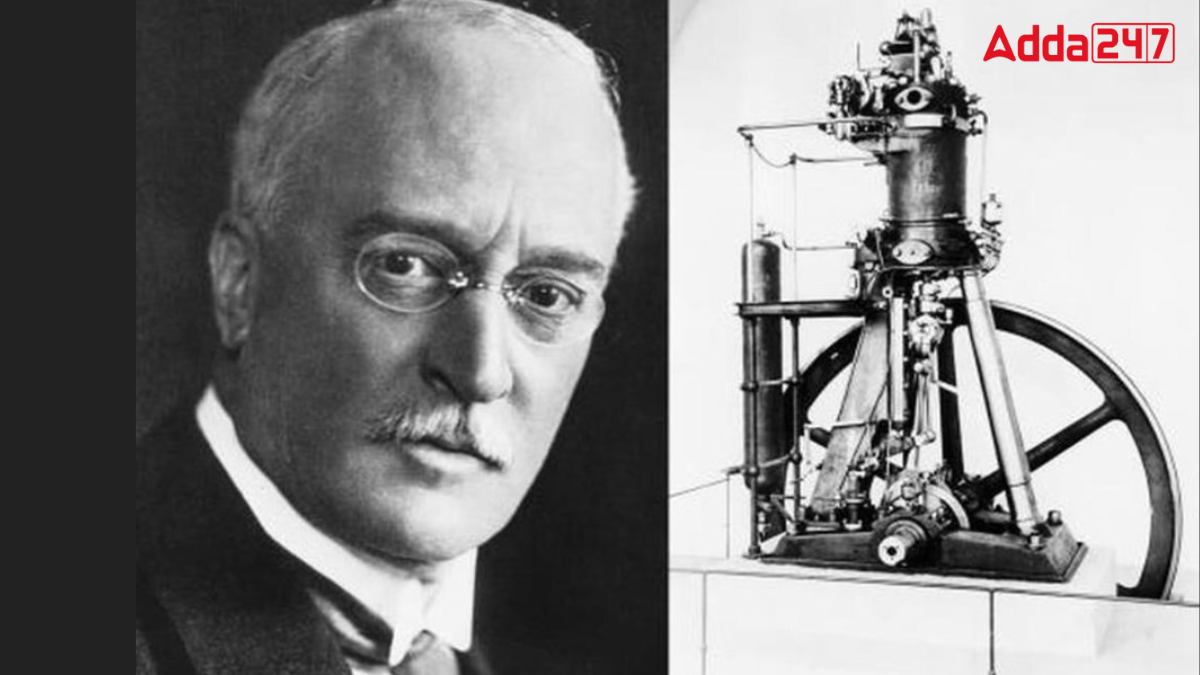
In the 1870s, steam engines were the primary source of power for factories and transportation. During this era, Rudolf Diesel, a student of thermodynamics, sought to create a more efficient engine. He envisioned an engine that would convert heat into power more effectively than existing technologies. By 1885, Diesel had established his workshop and began developing his engine, focusing on high compression for better efficiency.
First Diesel Engine Prototype
Rudolf Diesel received patents for his designs in the 1890s. The first prototype of the diesel engine was built in 1893. Despite initial setbacks, Diesel persevered. By 1897, he had achieved a significant milestone, producing an engine with 26.2% efficiency, which was 16.2% more efficient than the steam engines of that time.
How Does Engine Work?
Diesel engines operate using a four-stroke combustion cycle:
- Intake Stroke: Air enters the cylinders through the intake valve as the pistons move down.
- Compression Stroke: The pistons move up, compressing the air.
- Combustion Stroke: Fuel is injected and ignited by the heat of the compressed air, forcing the pistons down.
- Exhaust Stroke: The pistons move up again, pushing out the exhaust created during combustion.
This internal combustion process makes diesel engines more efficient than steam engines, which burn fuel outside the engine cylinders.
The Inventor of the Diesel Engine
Rudolf Diesel was passionate about engineering from a young age. At 14, he expressed his desire to become an engineer. After receiving a merit scholarship, Diesel studied at the Royal Bavarian Polytechnic of Munich. Under the mentorship of Carl von Linde, Diesel gained practical experience at an ice and refrigeration plant, where he developed an interest in fuel efficiency.
Diesel’s hard work led to the creation of his first prototype in 1893 and the successful diesel engine in 1897. Despite facing criticism and patent disputes, Diesel’s design proved to be more efficient and adaptable than others.
Diesel Engine Innovations
Over the years, numerous innovations have improved diesel engines:
- Turbocharging: In 1925, Alfred Büchi combined turbocharging with diesel engines, increasing efficiency by over 40%.
- Fuel-Injection Pumps: Introduced by Robert Bosch in 1927, these pumps improved fuel economy and efficiency.
- Passenger Vehicles: In 1936, Mercedes-Benz launched the first passenger vehicle with a diesel engine.
Diesel Engines Today
By the 1960s, diesel engines dominated the commercial trucking industry. The Clean Air Act of 1963 spurred advancements in diesel technology to reduce pollution. Modern diesel engines have incorporated various emission control technologies, focusing on fuel economy and environmental friendliness.



 Which Fish Can Produce Electricity?
Which Fish Can Produce Electricity?
 Which Place is known as the Denmark of I...
Which Place is known as the Denmark of I...
 Which Indian State is the Largest Produc...
Which Indian State is the Largest Produc...








