Madhya Pradesh, located in central India, is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and historical significance. Home to UNESCO World Heritage sites like Khajuraho and Sanchi, it boasts vibrant traditions, tribal art forms, and a plethora of wildlife sanctuaries. Let’s explore the northernmost district of Madhya Pradesh.
An Overview of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh, with a sprawling geographical area of 308,252 square kilometers, ranks as India’s second-largest state after Rajasthan. Its expanse constitutes 9.38% of the nation’s total geographical area. This central Indian state is renowned for its vast landscapes, cultural heritage, and significant contribution to the country’s geographical diversity and natural resources.
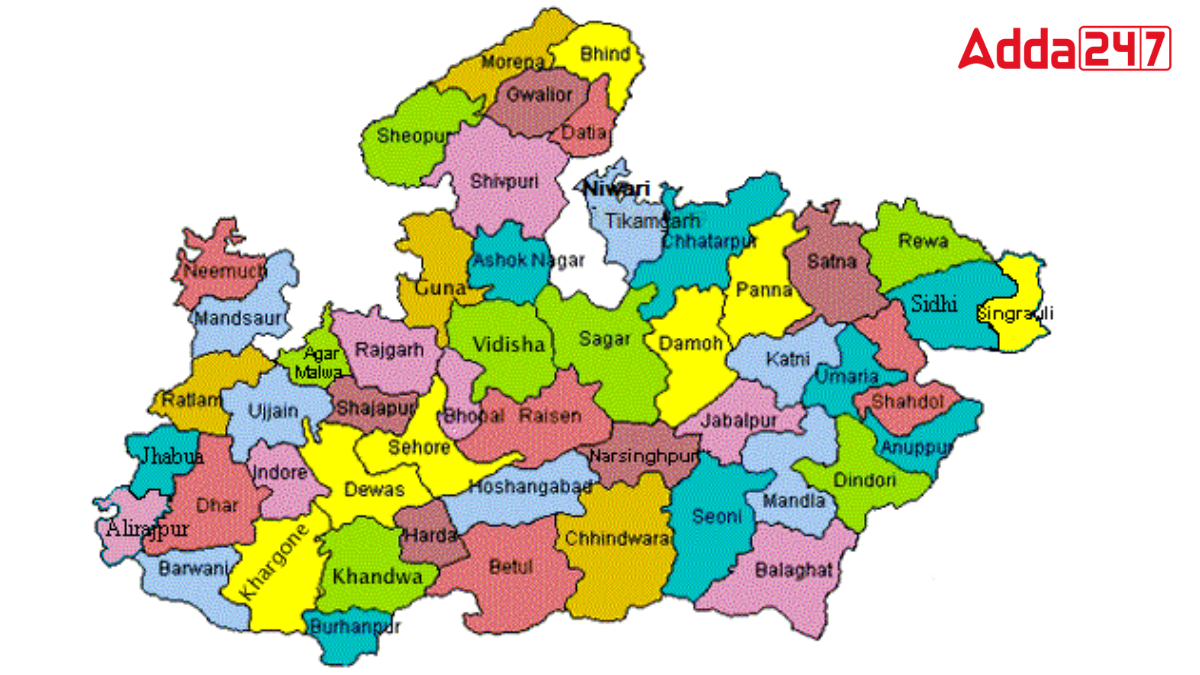
Districts in Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh, located at the heart of India, stands out as a hub of cultural variety. Covering a vast area of 308,000 square kilometers, the state comprises 55 districts, each with its distinct allure and importance. This article delves into exploring the cultural diversity and administrative complexities of these districts, which collectively shape Madhya Pradesh’s identity and development.
Geographical Extremes of Madhya Pradesh
Northernmost District: Morena
Southernmost District: Burhanpur
Easternmost District: Singrauli
Westernmost District: Alirajpur
Northernmost District of Madhya Pradesh
Morena District, the northernmost district of Madhya Pradesh, is known for its historical significance and natural beauty. It borders Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan, offering a blend of cultural influences. Morena is famous for the Chambal Valley, known for its rugged terrain and wildlife sanctuaries. The district’s economy revolves around agriculture, with prominent crops including wheat, barley, and mustard, reflecting its agricultural heritage and rural charm.
An Overview of Morena, the Northernmost District of Madhya Pradesh
Morena District, covering an area of 760 square kilometers, ranks as the second smallest district in Madhya Pradesh by land area. Despite its size, it is home to a significant population of approximately 1,965,970 people as of the 2011 census. The district is known for its agricultural productivity, cultural heritage, and strategic location on the border with Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan, contributing to its socio-economic diversity and importance in the region.



 Which Painting is known as the Indian Mo...
Which Painting is known as the Indian Mo...
 Which Indian State was the First to Chan...
Which Indian State was the First to Chan...
 Which Waterfall is known as the Monsoon ...
Which Waterfall is known as the Monsoon ...








