TSBIL stands for Translational Biomedical Imaging Laboratory. This special lab works to create new imaging techniques to better understand how the human and animal body works. The main aim is to use these new scientific methods in hospitals and clinics, so diseases can be found and treated more easily.
Full Form of TBIL
TBIL means Translational Biomedical Imaging Laboratory. It is a research center that works on creating modern imaging techniques to study the human and animal body. The goal is to turn these methods into practical tools for hospitals. These advanced images help doctors detect diseases early, understand them better, and treat patients in a safer and more effective way.
Main Goals of TBIL
The key goal of TBIL is to develop advanced imaging tools that help doctors diagnose and treat many different diseases. TBIL also wants to partner with other research centres to understand the human body better and discover new ways to treat illness. Another important aim is to teach students and researchers about biomedical imaging.
Research Areas in TBIL
TBIL does research in many areas of biomedical imaging. Some of them include:
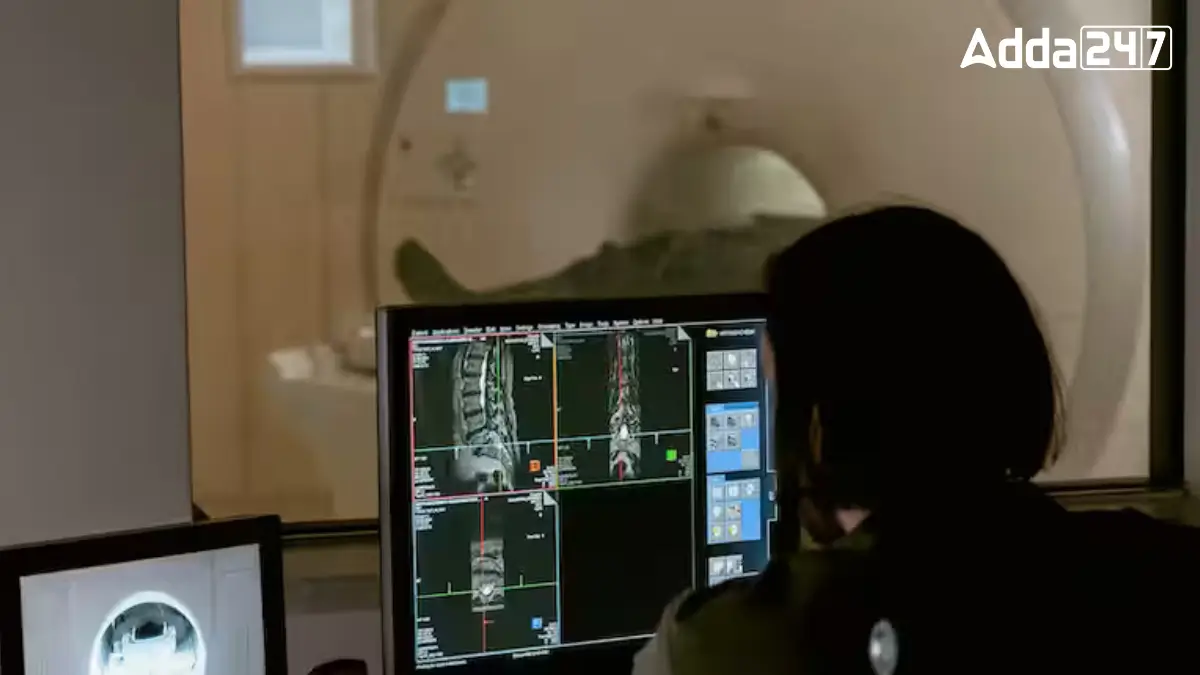
- MBI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI helps take detailed pictures of the inside of the body. TBIL is working on making MRI scans faster and clearer, so patients don’t have to stay in the machine for a long time.
- Optical Imaging: This technique is used to look at small things inside the body like cells and molecules. TBIL is developing new optical imaging tools to detect diseases like cancer early.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography): PET scans show how the body uses energy. TBIL researchers are making special PET tracers that can help find and treat many types of diseases.
- CT (Computed Tomography): CT scans also give detailed images of body parts. TBIL is trying to make CT scans safer by reducing the amount of radiation used.
Modern Equipment in TBIL
TBIL has many high-tech machines for research, including:
- MRI Scanner: A 3 Tesla MRI Scanner that gives very clear pictures of organs and tissues.
- Optical Imaging Tools: These include multiphoton and confocal microscopes to study cells and molecules.
- PET Scanner: Used to study how energy is used in the body.
- CT Scanner: Gives sharp and detailed images of the body’s internal structures.


 Which Country Officially Uses Two Differ...
Which Country Officially Uses Two Differ...
 Historic Glory! Jammu & Kashmir Win ...
Historic Glory! Jammu & Kashmir Win ...
 Three Major Inland Waterways Projects Op...
Three Major Inland Waterways Projects Op...








