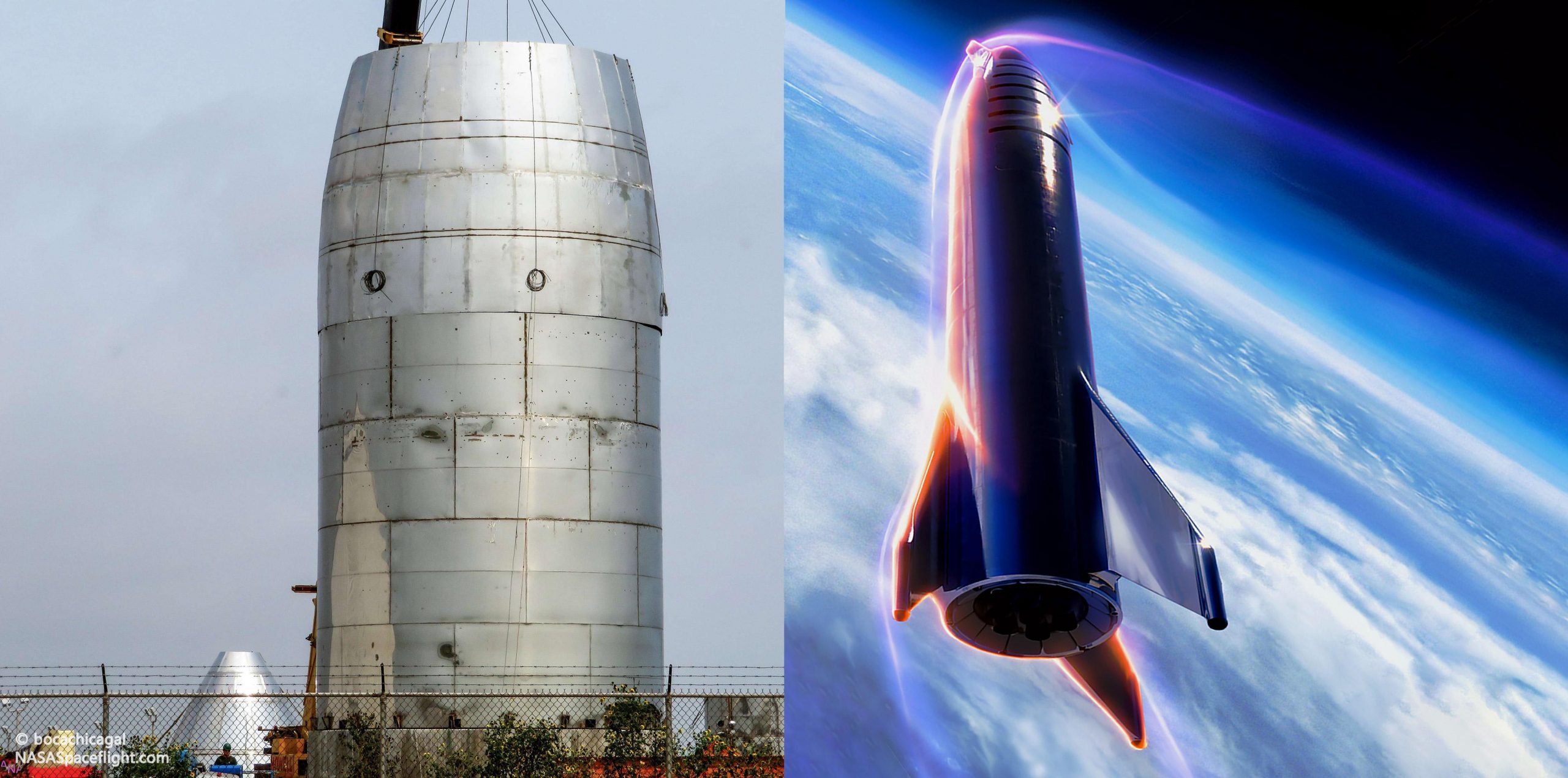
SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, is preparing to conduct an unprecedented test flight of its groundbreaking Starship, which is currently the most powerful rocket in existence. Ahead of the launch, Elon Musk has set modest expectations.
Buy Prime Test Series for all Banking, SSC, Insurance & other exams
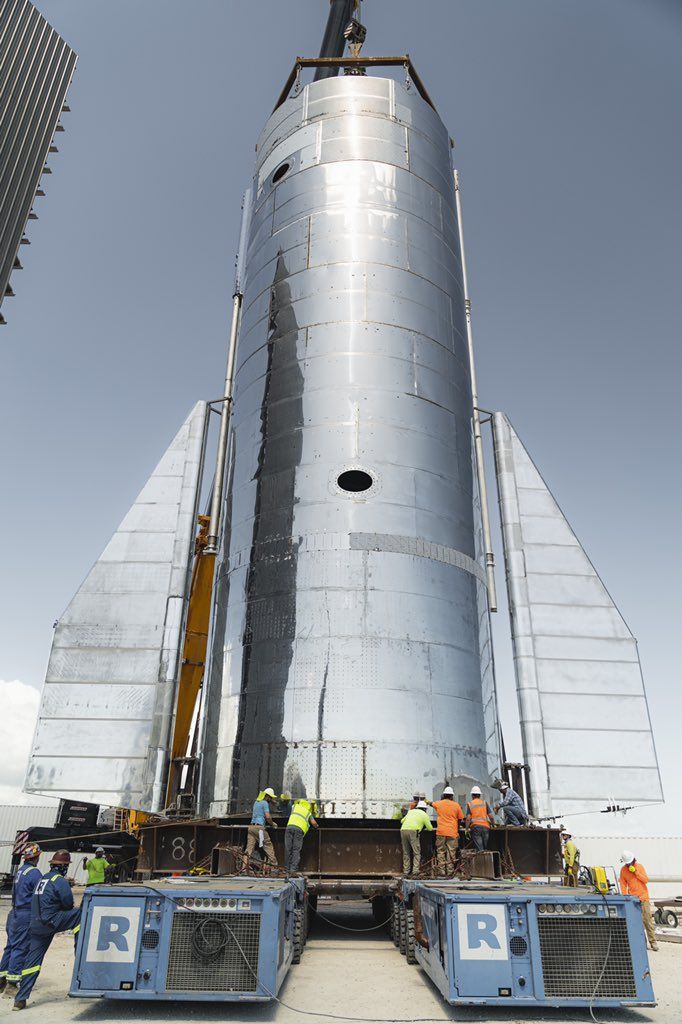

Key points about the first SpaceX launch of Starship:
- SpaceX is conducting a demonstration flight of its Starship rocket.
- This is the first time that both the Super Heavy first-stage rocket booster and the six-engine spacecraft will fly together.
- The upper-stage spacecraft had several unsuccessful flights before finally landing upright in 2021.
- SpaceX will not attempt to recover any part of the rocket or spacecraft; everything will fall into the sea.
- Starship has 33 main engines with a combined thrust of 16.7 million pounds.
- All but two of the methane-fueled first-stage engines were successfully tested on the launch pad in January.
- Starship has the capability to lift up to 250 tons and accommodate up to 100 people on a mission to Mars.
- Musk plans to launch Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit using the spacecraft before sending humans.
- Starship easily surpasses NASA’s Saturn V moon rocket and the Space Launch System of the Artemis program.
- It also outperforms the former Soviet Union’s ill-fated N1 moon rocket.
- The test flight will launch from a remote site near Boca Chica Beach in Texas.
- The flight will last 1 1/2 hours and will not complete a full orbit of the Earth.
- After three minutes of flight, the booster will separate and fall into the Gulf of Mexico.
- The spacecraft will continue eastward, crossing the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans before landing near Hawaii.
Main Aim of the Mission:
The objective of this mission is to validate the spacecraft’s capabilities, which Musk has designated as the primary vehicle for human exploration of the Moon and Mars.
The unmanned Starship is scheduled to take off as early as Monday, 17 April, ascending to an altitude of approximately 400 feet (120 meters) above the plains of South Texas. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has authorized the launch.
You may also read this:
NASA’s High-Resolution Air Quality Control Instrument Launches



 India Women's Hockey Qualified For Hocke...
India Women's Hockey Qualified For Hocke...
 Chhattisgarh Cabinet Approves Freedom of...
Chhattisgarh Cabinet Approves Freedom of...
 Which Place is known as the Denmark of I...
Which Place is known as the Denmark of I...








