The Indian government has issued a warning regarding a new and sophisticated scam known as “Smishing.” This term is a combination of “SMS” (Short Message Service) and “phishing,” signifying a malicious practice that exploits text messages to deceive individuals into divulging confidential information.
With the increasing reliance on mobile phones, smishing has emerged as a significant threat, necessitating individuals to remain vigilant and well-informed.
The Nature of Smishing Scams
Smishing scams often adopt a guise of legitimacy by posing as communication from trusted sources. Fraudulent messages may impersonate banks, government agencies, or well-known brands, creating a false sense of urgency that compels recipients to take immediate action. The ultimate goal is to trick individuals into revealing sensitive personal information.
Deceptive Tactics
These deceptive messages may request personal details such as credit card numbers, social security information, or login credentials. The pretext for these requests often revolves around security verification or account updates. To combat the rising tide of smishing, individuals are encouraged to report any incidents promptly.
Reporting Smishing Incidents
In the unfortunate event of falling victim to a smishing attack, individuals can take immediate action by dialing 1930 to report online financial fraud. Additionally, any instances of cybercrime can be reported at cybercrime.gov.in. Timely reporting is crucial to mitigating the impact of such scams and preventing further harm.
Precautionary Measures
As the saying goes, “precaution is better than treatment.” Therefore, it is imperative to exercise caution when dealing with text messages, especially those that are unsolicited. Avoid clicking on suspicious links and refrain from sharing personal information over text messages unless absolutely certain of the legitimacy of the communication.
Understanding Smishing: Unraveling the Mechanics
Definition and Origin
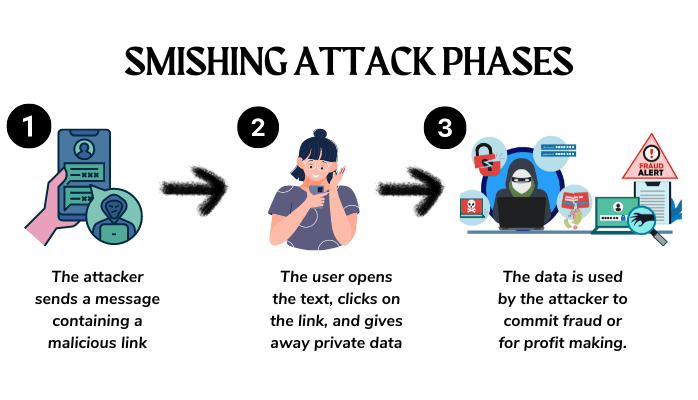
The term “smishing” is a portmanteau of “SMS” and “phishing.” It refers to a specific type of phishing attack that utilizes text messages instead of traditional emails to carry out fraudulent activities. While phishing typically involves email communication, smishing leverages the ubiquity of SMS for deceptive purposes.
Targeting Sensitive Information
Smishing attacks aim to extract sensitive personal information from unsuspecting individuals. Cybercriminals, engaged in smishing, seek to obtain passwords, credit card numbers, and other confidential data that can be exploited for financial gain or used to compromise the victim’s devices.
Operation of Smishing Attacks
Smishing messages are crafted with a sense of urgency or allure, prompting recipients to take immediate action. This action may involve clicking on a malicious link, calling a specified phone number, or providing sensitive information in response to the message.
The Fraudulent Facade
Once the victim succumbs to the urgency and interacts with the message, they are redirected to a deceptive website or mobile phone line designed to mimic a legitimate source. Here, the victim may be prompted to enter sensitive information, such as login credentials, social security numbers, credit card details, or personal identification numbers (PINs).
Exploitation and Consequences
Upon obtaining the victim’s sensitive information, the cybercriminal can exploit it for personal gain, committing fraud or compromising the victim’s device by installing malware. The consequences of falling prey to a smishing attack can be severe, emphasizing the need for heightened awareness and preventive measures.
Summary
- Smishing Warning: The Indian government has issued a warning about a rising threat known as “Smishing,” a blend of SMS and Phishing.Definition of Smishing: Smishing is a type of phishing attack using SMS instead of email, aiming to trick individuals into divulging sensitive personal information.
- Impersonation Tactics: Scammers masquerade as trusted entities like banks or government agencies, creating urgency in messages to prompt immediate responses.
- Information Requests: Smishing messages often request personal data, such as credit card numbers or login credentials, under the guise of security verifications or account updates.
- Operation of Smishing Attacks: Messages create urgency, prompting victims to click on malicious links or provide sensitive information, leading to fraudulent websites or phone lines.
- Consequences: Falling victim to smishing can result in financial fraud or device compromise, underscoring the importance of awareness and preventive measures in the face of evolving cyber threats
- Reporting Channels: Victims of smishing are urged to dial 1930 to report online financial fraud and can report cybercrimes at cybercrime.gov.in.
- Precautionary Measures: A proactive approach is recommended, advising individuals to refrain from clicking on suspicious links and avoid sharing personal information via unsolicited text messages.




 Sarvam AI Startup Program Launched to Bo...
Sarvam AI Startup Program Launched to Bo...
 IBM Launches First Infrastructure Innova...
IBM Launches First Infrastructure Innova...
 Kolli Hills Gets Tamil Nadu’s First Dark...
Kolli Hills Gets Tamil Nadu’s First Dark...








