Iran briefly shut down parts of the Strait of Hormuz during live-fire naval drills, instantly drawing global attention. Tehran described the restriction as a short safety measure, lasting only a few hours. However, the timing alongside escalating Iran-US tensions and renewed nuclear talks in Geneva amplified market anxieties. Even temporary disruptions in this narrow waterway can ripple through global oil flows, shipping costs, and energy prices. The episode underscored a critical reality: the world’s energy arteries remain highly vulnerable to geopolitical tensions in West Asia.
What Exactly Did Iran Do? – Iran Military Drills Explained
Iranian authorities temporarily restricted navigation,
- Conducted live surface firing exercises
- Launched missiles at designated targets
- Issued maritime safety advisories
- Shutdown lasted only several hours
Iran framed the move as a routine safety precaution, yet its rarity intensified global scrutiny.
Why Did Iran Restrict the Strait of Hormuz?
Several overlapping factors shaped the decision,
- Military Exercise Safety: Live-fire missile drills
- Strategic Signaling: Demonstrating regional control
- Iran-US Frictions: Heightened naval and drone incidents
- Diplomatic Context: Nuclear negotiations underway
Analysts interpret the move as both operational and symbolic — ensuring drill safety while projecting deterrence capability.
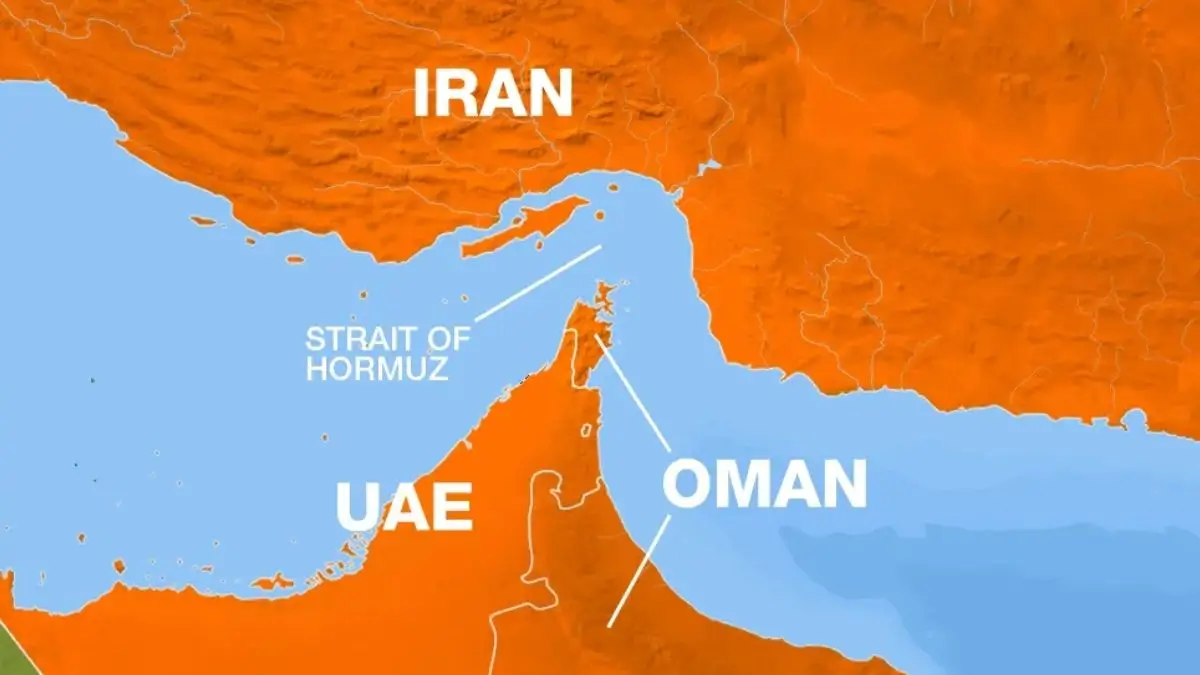
Why the Strait of Hormuz Matters for Global Oil Flows
The Strait of Hormuz is the world’s most critical maritime chokepoint,
- Connects Persian Gulf to Gulf of Oman and to the Indian Ocean
- Narrowest width: Nearly 33 km
- Handles ~13 million barrels/day (2025)
- Roughly 31% of global seaborne crude trade
Any restriction even perceived can shake energy markets.
Iran-US Tensions Behind the Backdrop
Recent incidents heightened friction,
- US interception of Iranian drone
- Maritime harassment reports
- Expanded US naval deployments
- Strategic posturing by both sides
These developments created a tense environment around the drills.
Nuclear Talks in Geneva – Progress or Deadlock?
Diplomatic engagement continued amid tensions,
- Mediated by Oman
- Discussions on nuclear limits vs sanctions relief
- Iran insists enrichment will continue
- Missile program deemed non-negotiable
- Encouraging remarks briefly cooled oil futures, but uncertainty persists.
Question
Q. The Strait of Hormuz connects the Persian Gulf to,
A) Red Sea
B) Gulf of Oman
C) Mediterranean Sea
D) Arabian Sea


 Gulf of Hormuz vs Strait of Malacca: Whi...
Gulf of Hormuz vs Strait of Malacca: Whi...
 Explained: Why Kharg Island Matters to G...
Explained: Why Kharg Island Matters to G...
 India-New Zealand Plan Major Sports Part...
India-New Zealand Plan Major Sports Part...








