Monetary policy tools are crucial instruments employed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to regulate the money supply, influence economic growth, and manage macroeconomic factors like inflation and unemployment. Divided into Quantitative and Qualitative categories, these tools play a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape of the country.
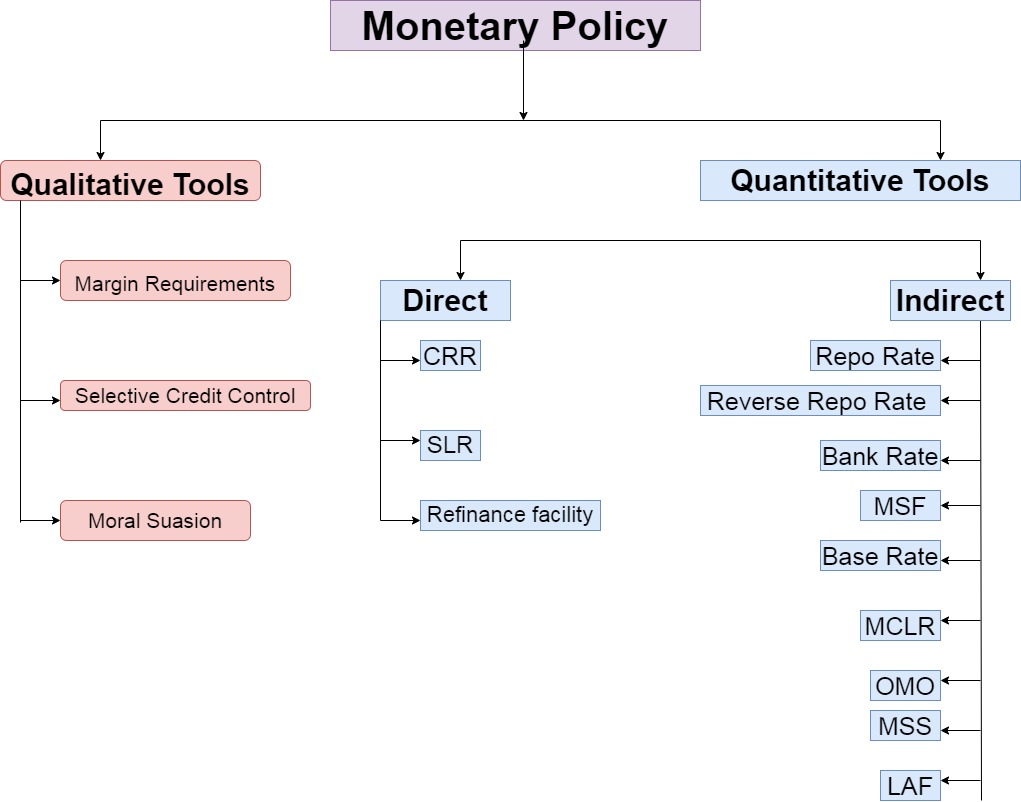
Quantitative Instruments:
1. Bank Rate:
- Definition: Rate at which RBI buys or rediscounts bills of exchange or commercial papers.
- Mandated by Section 49 of RBI Act, 1934.
- Aligned with MSF rate, changing automatically with policy repo rate adjustments.
2. Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR):
- Definition: Percentage of Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) banks must keep in liquid assets.
- Changes impact resource availability for private sector lending.
3. Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR):
- Definition: Average daily balance banks must maintain with RBI as a percentage of NDTL.
- Regulates liquidity in the banking system.
4. Repo Rate:
- Definition: Fixed interest rate at which RBI provides overnight liquidity to banks against collateral.
- Part of Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF).
5. Reverse Repo Rate:
- Definition: Fixed interest rate at which RBI absorbs liquidity from banks overnight.
- Also part of LAF.
6. Marginal Standing Deposit Facility (MSF):
- Definition: Allows banks to borrow additional overnight money from RBI using SLR portfolio.
- Acts as a safety valve for unexpected liquidity shocks.
Long-Term Repo Operation (LTRO):
-
-
- Utilizes repo rate for providing funds through one-year and three-year loans.
-
Open Market Operation (OMO):
-
-
- Involves purchase and sale of government securities to inject or absorb long-term liquidity.
-
Market Stabilisation Scheme (MSS):
-
-
- Introduced in 2004 to absorb surplus liquidity from capital inflows.
-
Qualitative Instruments:
1. Change in Marginal Requirement:
-
- Definition: Percentage of a loan not financed by the bank.
- Influences changes in loan sizes.
2. Regulation of Consumer Credit:
-
- Definition: Controls consumer credit through predetermined features of credit supply like instalment amount and loan period.
3. Rationing of Credit:
-
- Definition: Sets credit limits for commercial banks to control credit exposure and regulate bill rediscounting.
4. Moral Suasion:
-
- Definition: RBI’s recommendations to restrain credit during inflationary periods.
- Communicated through monetary policy expectations.
5. Direct Action:
-
- Definition: Imposes sanctions on banks for non-compliance with monetary policy guidelines.
- Example: Prompt Corrective Action Framework.
Questions Related to Exams
Q: What are monetary policy tools?
A: Instruments used by the central bank (RBI) to regulate money supply, stimulate economic growth, and control macroeconomic factors like inflation and unemployment.
Q: How does RBI use monetary policy tools in India?
A: To control money supply, RBI employs quantitative and qualitative tools, influencing factors such as interest rates, liquidity, and credit availability.
Q: What are Quantitative Instruments?
A: Tools linked to the quantity and volume of money, including Bank Rate, SLR, CRR, Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate, MSF, LTRO, OMO, and MSS.
Q: What are Qualitative Instruments?
A: Selective tools regulating different types of credit, like Consumer Credit Regulation, Rationing of Credit, Moral Suasion, and Direct Action.
Q: How does Bank Rate function?
A: It is the rate at which RBI buys or rediscounts bills, aligned with MSF rate, automatically changing with policy repo rate adjustments.
Q: What is SLR, and how does it impact the economy?
A: SLR is the percentage of NDTL banks must keep in liquid assets. Changes affect resource availability in the banking system for lending.
Q: What is the purpose of CRR?
A: CRR mandates banks to maintain a daily balance with RBI, influencing liquidity in the banking system.
Q: Explain Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate.
A: Repo Rate is the fixed interest rate for RBI to provide overnight liquidity to banks. Reverse Repo Rate is the rate at which RBI absorbs liquidity from banks overnight.
Q: What is MSF, and how does it act as a safety valve?
A: MSF allows banks to borrow overnight money from RBI using SLR portfolio, acting as a safety valve for unexpected liquidity shocks.
Q: What role do qualitative instruments play?
A: They regulate specific types of credit, control credit exposure, and influence credit behavior through tools like Moral Suasion and Direct Action.
Q: How does RBI use OMO and MSS for monetary management?
A: OMO involves outright purchase and sale of government securities to inject or absorb long-term liquidity. MSS, introduced in 2004, absorbs surplus liquidity from capital inflows.
Q: What is the Prompt Corrective Action Framework?
A: It’s a Direct Action measure where RBI imposes sanctions on banks for not following monetary policy guidelines, ensuring compliance.




 PhonePe Launches AI-Powered Natural Lang...
PhonePe Launches AI-Powered Natural Lang...
 ICICI’s New Swasthya Pension Scheme: A S...
ICICI’s New Swasthya Pension Scheme: A S...
 RBI’s New Rulebook: UTI Required for All...
RBI’s New Rulebook: UTI Required for All...








