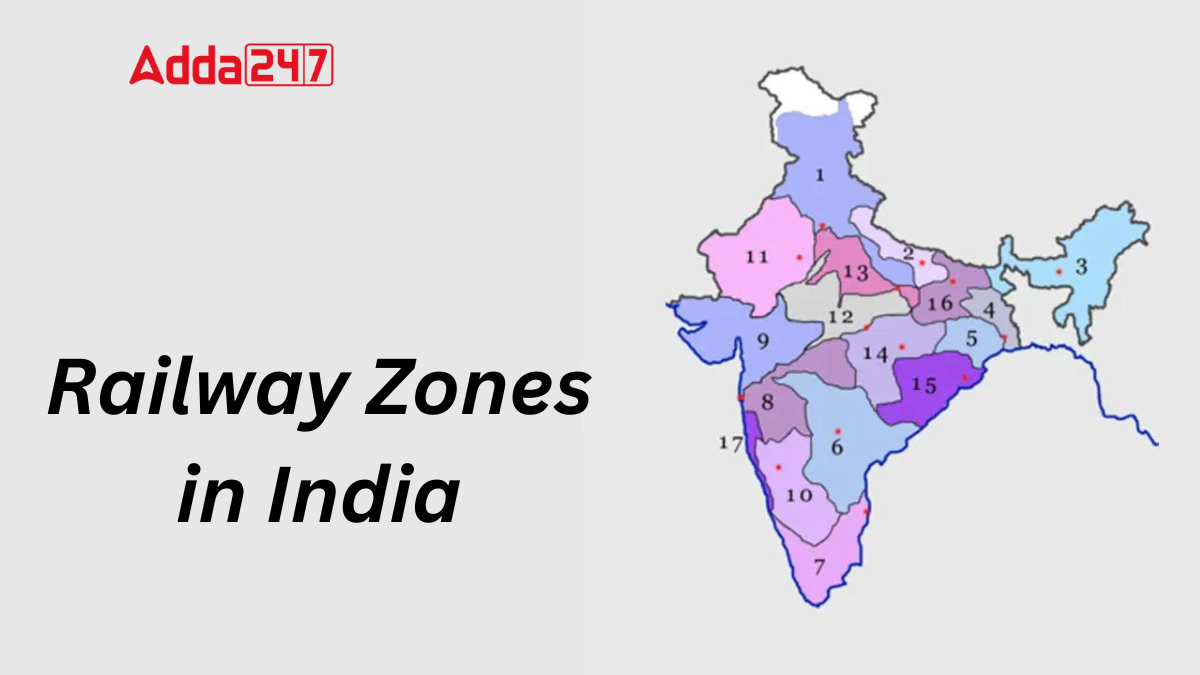
India’s railway network is one of the largest in the world, and it is divided into several zones to manage its vast operations efficiently. Each zone is responsible for specific geographical regions and has its own headquarters. Here’s a look at the railway zones of India and their respective headquarters:
How Many Railway Zones are there in India?
India has 18 railway zones, each with its own headquarters. These zones include Central Railway, Eastern Railway, Western Railway, and others. Each zone is responsible for managing and operating a specific region of the railway network. Additionally, there is a 19th zone, Metro Railway, which operates separately. This zonal system ensures efficient administration and smooth functioning of India’s vast railway network.
List of Railway Zones of India and Their Headquarters
Indian Railways is divided into 18 main zones, with each zone having a designated headquarters. Here is the list of 18 railway zones of India with their respective headquarters:
| Railway Zone | Headquarter |
| Central Railway | Mumbai |
| East Central Railway | Hajipur |
| East Coast Railway | Bhubaneswar |
| Eastern Railway | Kolkata |
| Konkan Railway | Navi Mumbai |
| North Central Railway | Prayagraj |
| North Eastern Railway | Gorakhpur |
| North Western Railway | Jaipur |
| Northeast Frontier Railway | Guwahati |
| Northern Railway | Delhi |
| South Central Railway | Secunderabad |
| South Coast Railway | Visakhapatnam |
| South East Central Railway | Bilaspur |
| South Eastern Railway | Kolkata |
| South Western Railway | Hubballi |
| Southern Railway | Chennai |
| West Central Railway | Jabalpur |
| Western Railway | Mumbai |
Need for Railway Zones
Initially, Indian Railways was divided into regions. However, as passenger numbers increased and the network expanded, it became necessary to create smaller, more manageable divisions. These divisions were further organized into zones, each managed by a senior official to ensure smooth and effective operation of the railway services.



 Who Presides over the Lok Sabha Meetings...
Who Presides over the Lok Sabha Meetings...
 Top-5 Plum Producing States of India, Kn...
Top-5 Plum Producing States of India, Kn...
 Difference Between Metallic Minerals and...
Difference Between Metallic Minerals and...


