The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a crucial tool for assessing and communicating the quality of the air we breathe. It provides valuable information about the levels of various air pollutants, helping individuals and communities make informed decisions to protect their health. This article explores the aqi, its significance, and how it operates to provide a clear understanding of air quality.
AQI- Air Quality Index
The Air Quality Index, commonly known as the aqi, is a standardized scale used to measure and report the quality of the air in a specific location. It quantifies the concentration of various air pollutants in the atmosphere and translates this data into a simple numerical value, making it easier for the public to grasp the severity of air pollution.
The concentrations of the pollutants are measured in ppm or parts per million. The index is calculated from the concentrations of the following pollutants: Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulphur Dioxide, PM2.
AIQ Full Form
AQI Full form is air quality index (AQI) is an index for reporting air quality on a daily basis.
How Does the AQI Work?
The aqi relies on data collected from air quality monitoring stations strategically located in different areas. These stations continuously measure the concentration of key air pollutants, including:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): Tiny airborne particles that can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially causing respiratory problems.
- Ground-Level Ozone (O3): Ozone at ground level is a harmful pollutant that can cause breathing difficulties and other health issues.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): A gas produced by combustion processes that can irritate the respiratory system.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): A gas that can harm the respiratory system and contribute to the formation of acid rain.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas that interferes with the body’s ability to transport oxygen.
The aqi considers the concentration levels of these pollutants and calculates a numerical value. This value is then classified into specific color-coded categories, which represent different levels of air quality, ranging from “Good” to “Hazardous.” The higher the aqi value, the worse the air quality.
AQI Levels
Check All AQI Levels,
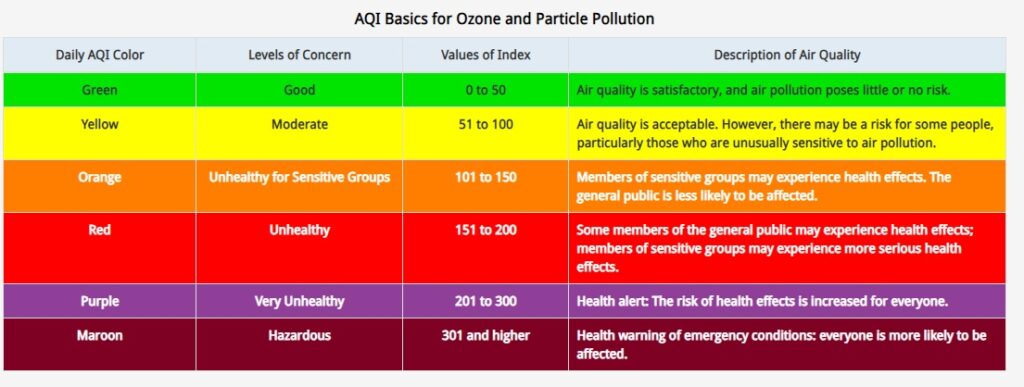
-
Good (0-50):
Air Quality: Satisfactory.
Precautions: No specific precautions needed. Air quality poses little or no risk to health.
-
Moderate (51-100):
Air Quality: Acceptable.
Precautions: Generally safe, but individuals with respiratory conditions may experience minor discomfort. Limit outdoor activities during high pollutant hours.
-
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups (101-150):
Air Quality: Unhealthy for sensitive individuals.
Precautions: People with respiratory or heart conditions, children, and older adults should reduce prolonged or heavy outdoor exertion. The general public is not likely to be affected.
-
Unhealthy (151-200):
Air Quality: Unhealthy.
Precautions: Everyone may begin to experience health effects. Sensitive groups may experience more severe symptoms. Limit outdoor activities and stay indoors, especially during peak pollution hours.
-
Very Unhealthy (201-300):
Air Quality: Very unhealthy.
Precautions: Health alert – everyone may experience more serious health effects. Avoid outdoor activities and stay indoors.
-
Hazardous (301-500):
Air Quality: Hazardous.
Precautions: Health warnings of emergency conditions. The entire population is likely to be affected. Stay indoors, keep windows closed, and use air purifiers if available.
Calculating the AQI
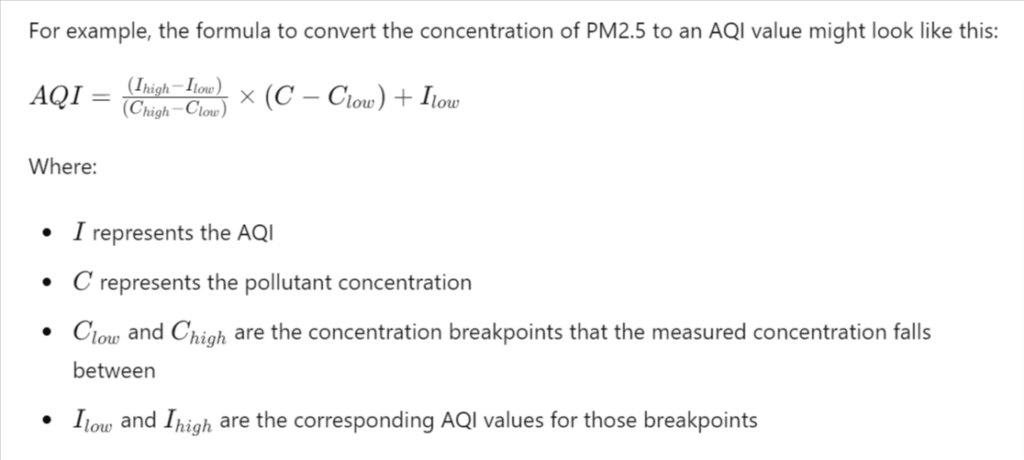
The AQI calculation involves converting the concentrations of air pollutants into a standardized index. This process uses specific breakpoints, which are concentration ranges corresponding to the AQI scale. For each pollutant, the following steps are generally followed:
- Measure the Concentration: Determine the concentration of each pollutant in the air, typically averaged over a specific period (e.g., 24 hours for PM2.5).
- Apply the Formula: Use the AQI formula to convert the pollutant concentration into an AQI value.
- Identify the Highest Value: The highest AQI value among the pollutants is taken as the overall AQI for that location and time.
AIR Health Effects and Recommendations
Good (0-50)
- Health Effects: Minimal impact.
- Recommendations: No precautions needed.
Moderate (51-100)
- Health Effects: Minor respiratory discomfort for sensitive individuals.
- Recommendations: Unusually sensitive people should consider limiting prolonged outdoor exertion.
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups (101-150)
- Health Effects: Increased likelihood of adverse health effects for sensitive groups.
- Recommendations: Sensitive individuals should reduce prolonged outdoor exertion.
Unhealthy (151-200)
- Health Effects: Everyone may experience health effects; sensitive groups may experience more serious effects.
- Recommendations: All individuals, particularly sensitive groups, should limit prolonged outdoor exertion.
Very Unhealthy (201-300)
- Health Effects: Serious health effects for everyone.
- Recommendations: Everyone should avoid prolonged outdoor exertion; sensitive groups should remain indoors.
Hazardous (301-500)
- Health Effects: Emergency conditions; significant health risk for everyone.
- Recommendations: Everyone should avoid all outdoor exertion; sensitive groups should remain indoors and keep activity levels low.
AIR Global Standards and Variations
Different countries and regions may use slightly different methods to calculate and report the AQI, based on local environmental regulations and standards. For instance:
- United States: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides daily AQI updates and has established specific guidelines for various pollutants.
- Europe: The European Environment Agency (EEA) monitors air quality and reports AQI using the Common Air Quality Index (CAQI).
- China: The Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) uses its own AQI system, with different breakpoints and pollutant considerations.
The Significance of the AQI
- Health Protection: The primary aim of the aqi is to safeguard public health. It offers warnings and guidance to people, especially those with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions, enabling them to take precautions during times of poor air quality.
- Environmental Awareness: The aqi educates the public about air pollution and its environmental impact, encouraging individuals and communities to make environmentally responsible choices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies use the aqi to monitor compliance with air quality standards and to implement pollution control measures.
- Emergency Response: During episodes of extreme air pollution, the aqi provides a basis for emergency responses, such as issuing advisories or restricting outdoor activities.
Precautions During Poor Air Quality
- Stay Informed: Regularly check the aqi for your area via local news, apps, or websites.
- Limit Outdoor Activities: Reduce time spent outdoors during higher aqi levels, especially for sensitive groups.
- Use Air Filters: If available, use air purifiers with HEPA filters to improve indoor air quality.
- Close Windows and Doors: Seal windows and doors to prevent outdoor pollutants from entering.
- Wear Masks: If necessary, use N95 respirators to filter out harmful particles when air quality is hazardous.
The Importance of AQI
The AQI serves several critical functions:
- Public Health Protection: By informing the public about current air quality and potential health risks, the AQI helps individuals take appropriate actions to protect their health.
- Environmental Awareness: It raises awareness about air pollution and encourages actions to reduce emissions.
- Policy and Regulation: The AQI data helps policymakers design and implement regulations to improve air quality and mitigate pollution sources.
AIR Quality Index Chart- AQI Chart
Here is a detailed Air Quality Index (AQI) chart that outlines the different categories, their corresponding AQI values, associated health concerns, and recommendations for each category:
| AQI Category | AQI Range | Color Code | Health Concern | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good | 0-50 | Green | Air quality is satisfactory, and air pollution poses little or no risk. | No precautions needed. |
| Moderate | 51-100 | Yellow | Air quality is acceptable; however, for some pollutants, there may be a moderate health concern for a very small number of people who are unusually sensitive to air pollution. | Unusually sensitive people should consider limiting prolonged outdoor exertion. |
| Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups | 101-150 | Orange | Members of sensitive groups may experience health effects. The general public is not likely to be affected. | Sensitive individuals should reduce prolonged outdoor exertion. |
| Unhealthy | 151-200 | Red | Everyone may begin to experience health effects; members of sensitive groups may experience more serious health effects. | Everyone should limit prolonged outdoor exertion. |
| Very Unhealthy | 201-300 | Purple | Health alert: everyone may experience more serious health effects. | Everyone should avoid prolonged outdoor exertion; sensitive groups should remain indoors. |
| Hazardous | 301-500 | Maroon | Health warnings of emergency conditions. The entire population is more likely to be affected. | Everyone should avoid all outdoor exertion; sensitive groups should remain indoors and keep activity levels low. |
AQI Color Codes and Visualization
The color codes in the AQI chart help visually indicate the severity of air pollution levels:
- Green (Good): Low pollution.
- Yellow (Moderate): Acceptable pollution levels.
- Orange (Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups): Moderate pollution posing health risks to sensitive groups.
- Red (Unhealthy): High pollution with health risks for everyone.
- Purple (Very Unhealthy): Very high pollution posing serious health risks.
- Maroon (Hazardous): Extremely high pollution with emergency conditions.
Using the AQI
To use the AQI effectively, individuals should:
- Monitor Daily AQI Levels: Check local AQI reports regularly, especially if you belong to a sensitive group.
- Follow Health Recommendations: Adhere to the health recommendations provided for the AQI category in your area.
- Take Preventive Actions: Reduce exposure to polluted air by staying indoors, using air purifiers, and avoiding outdoor activities when AQI levels are high.
AQI India
In India, the Air Quality Index (AQI) is monitored and reported by various agencies, including the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and state pollution control boards. The AQI system in India provides a comprehensive measure of air quality, helping to inform the public about the health impacts of air pollution.
Key Pollutants in India’s AQI
The AQI in India considers eight pollutants:
- Particulate Matter (PM10)
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5)
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂)
- Ozone (O₃)
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂)
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Ammonia (NH₃)
- Lead (Pb)
AQI Categories in India
The AQI is divided into six categories, each corresponding to a different level of health concern:
| AQI Category | AQI Range | Color Code | Health Concern | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good | 0-50 | Green | Minimal impact. | No precautions needed. |
| Satisfactory | 51-100 | Light Green | Minor breathing discomfort to sensitive people. | Avoid prolonged outdoor exertion if you are unusually sensitive. |
| Moderate | 101-200 | Yellow | Breathing discomfort to people with lung disease, children, and older adults. | Sensitive individuals should limit prolonged outdoor exertion. |
| Poor | 201-300 | Orange | Breathing discomfort to most people on prolonged exposure. | Everyone should limit prolonged outdoor exertion. |
| Very Poor | 301-400 | Red | Respiratory effects even on healthy people, serious impact on people with lung/heart disease. | Avoid outdoor activities, especially sensitive groups. |
| Severe | 401-500 | Maroon | Affects healthy people and seriously impacts those with existing diseases. | Avoid all outdoor exertion, sensitive groups should remain indoors. |
AQI Health Impacts and Recommendations in India
Good (0-50)
- Health Effects: Air quality is considered satisfactory with little or no risk.
- Recommendations: No precautions needed.
Satisfactory (51-100)
- Health Effects: Minor breathing discomfort to sensitive people.
- Recommendations: Unusually sensitive people should consider limiting prolonged outdoor exertion.
Moderate (101-200)
- Health Effects: Breathing discomfort to people with lung disease, children, and older adults.
- Recommendations: Sensitive groups should limit prolonged outdoor exertion.
Poor (201-300)
- Health Effects: Breathing discomfort to most people on prolonged exposure.
- Recommendations: Everyone should limit prolonged outdoor exertion.
Very Poor (301-400)
- Health Effects: Respiratory effects even on healthy people, serious impact on people with lung/heart disease.
- Recommendations: Avoid outdoor activities, especially for sensitive groups.
Severe (401-500)
- Health Effects: Affects healthy people and seriously impacts those with existing diseases.
- Recommendations: Avoid all outdoor exertion, sensitive groups should remain indoors.
Monitoring and Reporting
In India, air quality is monitored through a network of monitoring stations across major cities and towns. The data collected is made available to the public through various platforms, including the CPCB website, mobile apps like “SAFAR-Air” (System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research), and other state-specific portals.
Major Contributors to Air Pollution in India
Several factors contribute to high levels of air pollution in India:
- Vehicle Emissions: A major source of air pollution, especially in urban areas.
- Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants emit large quantities of pollutants.
- Construction Dust: Construction activities contribute significantly to particulate matter in the air.
- Burning of Biomass: Agricultural practices, such as stubble burning, and burning of household waste.
- Natural Factors: Dust storms and other natural phenomena.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has initiated several programs to combat air pollution:
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): Launched in 2019, aiming to reduce PM2.5 and PM10 levels by 20-30% by 2024.
- Odd-Even Scheme: Implemented in cities like Delhi to reduce vehicle emissions.
- Promotion of Public Transport: Encouraging the use of public transport and electric vehicles.
- Industrial Regulation: Stricter emission norms for industries.
Conclusion for Good Air Quality Index
Understanding the Air Quality Index (AQI) is essential for making informed decisions about outdoor activities and personal health, especially for vulnerable populations. By providing a clear and standardized measure of air pollution levels, the AQI plays a crucial role in public health, environmental awareness, and policy-making. It is a vital tool in the global effort to monitor and improve air quality for the well-being of all.








 Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai Hits $1.1 Bil...
Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai Hits $1.1 Bil...
 Puducherry Becomes First State to Integr...
Puducherry Becomes First State to Integr...
 Ancient Egyptian Genome Sequenced for th...
Ancient Egyptian Genome Sequenced for th...

