Did you know your brain is the most complex organ in your body? It controls your thoughts, memory, emotions, and even the smallest body movements without you noticing. From blinking to dreaming, everything depends on different brain regions working together.
Some parts help you breathe and keep your heart beating, while others help you solve maths, recognize faces, and learn new things. Each section has its own special job, just like members of a team.
Scientists often compare the brain to a supercomputer because it can process information very fast. But interestingly, not all parts of the brain are the same size — some are much larger because they handle more complex activities.
The biggest region is responsible for thinking, learning, understanding language, and making decisions. It also helps shape your personality and behaviour, which makes humans unique among living beings.
In the next section, you’ll discover which specific brain part holds this important role and why it is so large.
What is the Largest Part of the Brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It forms about 85% of the total brain weight and lies at the top of the head, above the brainstem and cerebellum.
This is the thinking part of the brain. It allows humans to reason, make decisions, remember experiences, and control voluntary actions. Because of the cerebrum, humans can learn new skills, create art, and communicate through language.
Main Functions of the Cerebrum
The cerebrum works like the body’s main command office. It manages both physical and mental activities.
1. Thinking and Intelligence
It helps in learning, understanding, analysing, and solving problems. All logical reasoning and creativity happen here.
2. Memory Storage
The cerebrum stores short-term and long-term memories such as names, places, and experiences.
3. Sensory Processing
It receives signals from:
- Eyes (vision)
- Ears (sound)
- Nose (smell)
- Skin (touch)
- Tongue (taste)
Then it interprets what these signals mean.
4. Movement Control
All voluntary movements — walking, writing, speaking, or typing — are controlled by the cerebrum.
5. Emotions and Speech
Feelings like happiness, anger, fear, and excitement are processed here. It also allows us to form words and understand language.
Structure of the Cerebrum
The cerebrum looks like a large wrinkled walnut. The folds are very important because they increase the brain’s surface area.
Important Surface Features:
- Gyri – Raised ridges
- Sulci – Shallow grooves
- Fissures – Deep grooves dividing major sections
These folds allow billions of neurons to fit inside the skull.
Two Hemispheres of the Cerebrum
The cerebrum is divided into left and right halves, called hemispheres. They are connected by a thick band of nerve fibres known as the corpus callosum. This connection helps both sides share information.
Left Hemisphere (Logical Side)
- Language and grammar
- Mathematics
- Reasoning
- Controls right side of body
Right Hemisphere (Creative Side)
- Imagination
- Music and art
- Understanding emotions and tone
- Controls left side of body
Both sides work together — one cannot function properly without the other.
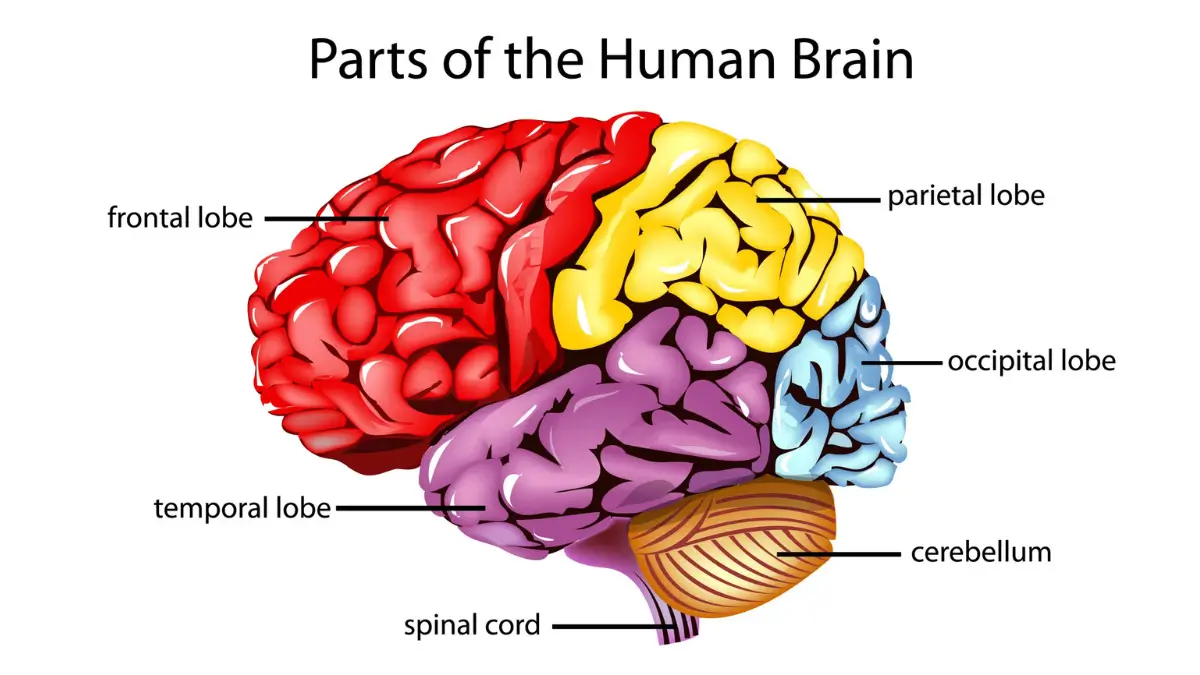
Four Lobes of the Cerebrum and Their Functions
Each hemisphere is further divided into four parts called lobes.
1. Frontal Lobe (Front Part)
Responsible for:
- Decision making
- Planning
- Personality
- Voluntary movement
- Speaking
2. Parietal Lobe (Top Middle)
Responsible for:
- Touch and pressure
- Temperature and pain
- Understanding position and direction
3. Temporal Lobe (Side Near Ears)
Responsible for:
- Hearing
- Memory
- Understanding language
4. Occipital Lobe (Back Part)
Responsible for:
- Vision
- Identifying shapes and colours
Why the Cerebrum is Important?
The cerebrum is what makes humans different from most animals. It allows advanced thinking, communication, and emotional understanding. Even a small injury to certain areas can change personality, behaviour, or memory.


 Which Place is known as the Diamond Capi...
Which Place is known as the Diamond Capi...
 List of Major LPG Gas Companies in India...
List of Major LPG Gas Companies in India...
 Which Fish Can Produce Electricity?
Which Fish Can Produce Electricity?








