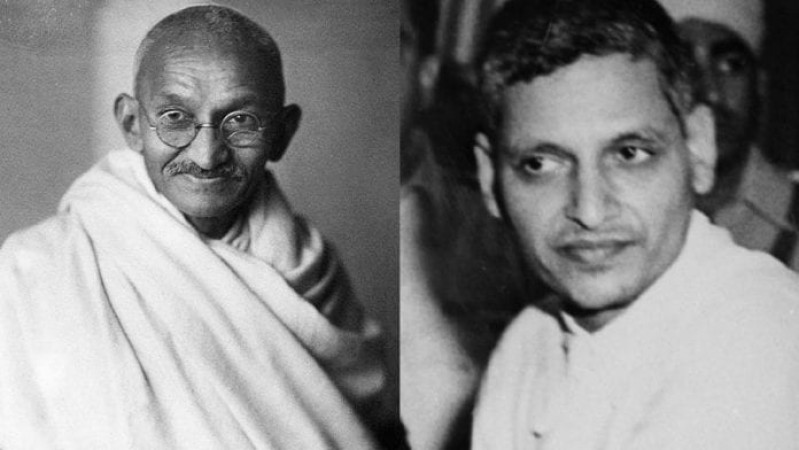
Death of Mahatma Gandhi
The death of Mahatma Gandhi on 30 January 1948 by a Hindu Nationalist, Nathuram Godse, remains a haunting and tragic event in the history of India’s fight for Independence. The man who had preached nonviolent resistance and won hearts with his principles was taken away by an act of violence.
Who was Nathuram Godse?
Nathuram Godse, also known as Ramachandra Vinayak Godse, hailed from Maharashtra and was a Hindu nationalist. Born into a Brahmin family in Baramati, Pune, he was given the name “Nathuram” due to a family belief that wearing nose ring would protect him from a curse that took the lives of his male siblings in infancy.
An Unsettles Journey of Nathuram Godse
Godse’s educational journey was marked by a shift from local schooling to an English-language institution in Pune. However, he dropped out to become an activist, later joining the ranks of Hindu Mahasabha. In his early years, he held respect for Mahatma Gandhi and ever participated in the Civil Disobedience Movement in 1930.
Shift in Ideals and Involvement
Inspired by nationalist ideas advocated by Vinayaka Damodar Savarkar, Godse’s beliefs took a different turn. He became a member of Hindu Mahasabha and voices his toughts through newspaper articles. With his partner Narayan Apte, he founded the newspaper “Agrani” and served as its editor.
Three attempts, One Tragic Success
Godse made two unsuccessful efforts in 1944. However, on January 30, 1948, during a multi-faith prayer meeting at Birla House, New Delhi, he fatally shot Gandhi three times at close range, leading to the leader’s tragic demise.
Post-event, Godse claimed that Gandhi favored the political demands of British India’s Muslims during the tumultuous 1947 partition. This belief played a significant role in his decision to take such a drastic step.
Arrest, Trial and Sentence
Godse’s act led to his arrest and a trial at the Punjab High Court in Shimla. Despite pleas for leniency from Mahatma Gandhi’s sons, his sentence was upheld. On November 15, 1949, he was executed at Ambala Central Jail.
Legacy
The assassination of Mahatma Gandhi by Nathuram Godse remains a solemn chapter in India’s history. Godse’s transformation from a Gandhi supporter to a radical activist emphasizes the intricate nature of ideological changes and the grave outcomes of extreme deeds. This occurrence highlights the significance of harmonious discourse and empathy in moulding a fair society.




 Weekly One Liners 02nd to 08th of Februa...
Weekly One Liners 02nd to 08th of Februa...
 Who has Won the Most Grammy Awards? Know...
Who has Won the Most Grammy Awards? Know...
 How Many States are There in India? Chec...
How Many States are There in India? Chec...








