Scientists have discovered a previously unknown species of mushroom in the Himalayan forests of Uttarakhand. Found growing beneath oak trees at high altitude, the new species adds a fresh chapter to India’s fungal diversity and marks the first official record of its genus in the country.
Why in News?
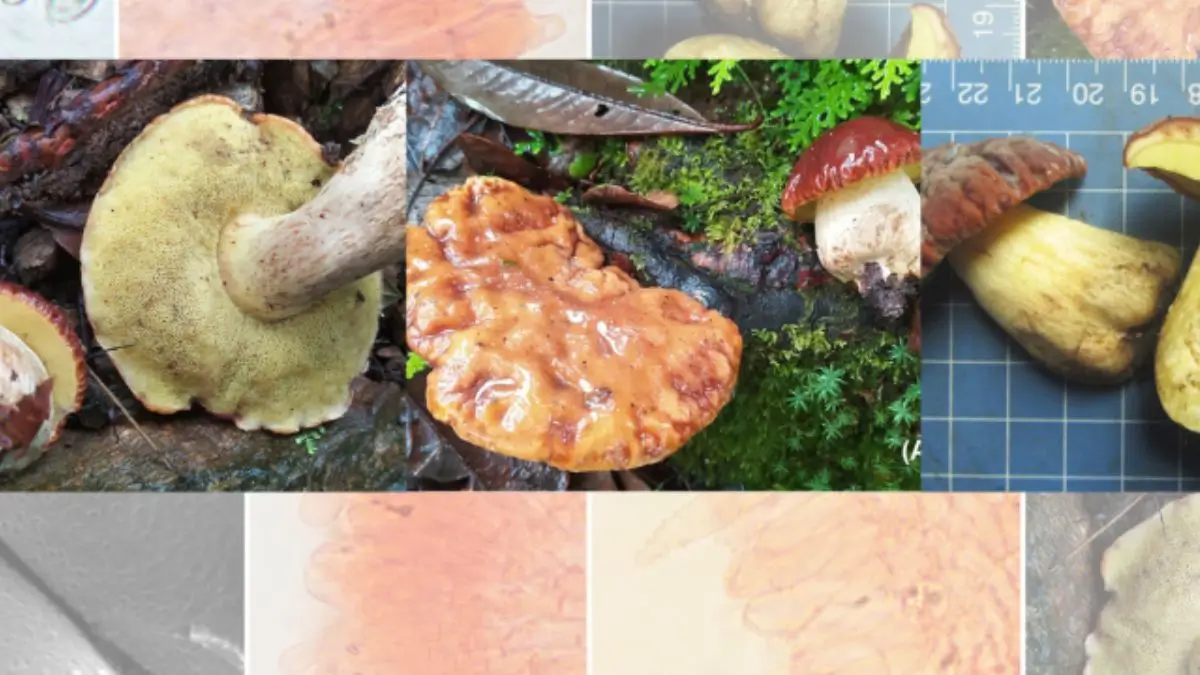
Researchers have identified a new pitted-spore mushroom species named Hemileccinum indicum in the oak forests of Uttarakhand. The discovery, made during field studies in 2022–23, represents the first time the genus Hemileccinum has been recorded in India.
Where and How Was the Mushroom Discovered?
- The mushroom was found in the Bageshwar district, specifically in the Dhakuri region, located at an altitude of over 2,600 metres in the Indian Himalayas.
- The discovery was made during macrofungal forays, which are systematic field explorations conducted during the monsoon season to document large fungi.
- These surveys were carried out by researchers from the Botanical Survey of India, the University of Torino, and St. Xavier’s College.
Why Is Hemileccinum indicum a Big Scientific Find?
- Although the mushroom initially resembled similar species found in North America and China, advanced testing revealed it to be completely new.
- Using multigene molecular phylogenetic analysis, scientists compared its DNA with known species worldwide.
- The results showed that while it is closely related to a species from Florida, it has a distinct genetic identity.
- This confirms it as a new branch in the fungal evolutionary tree and significantly expands the known global range of the Hemileccinum genus.
Unique Physical and Microscopic Features
- Hemileccinum indicum belongs to a group called boletes, mushrooms that have pores instead of gills beneath their caps.
- It has a wrinkled violet-brown cap that turns leathery brown as it matures and a pastel yellow pore surface that does not change colour when bruised.
- Its most striking feature appears under a Scanning Electron Microscope, where the spores show tiny, intricate pits.
- These pitted spores and a smooth stem clearly distinguish it from related species, which usually have smooth spores or scaly stems.
Ecological Importance of the Discovery
- Ecologically, this mushroom is ectomycorrhizal, meaning it forms a mutually beneficial relationship with tree roots.
- In this case, it partners with Quercus species. Such fungi help trees absorb nutrients and water while receiving sugars in return.
- This underground cooperation strengthens forest health, soil stability, and nutrient cycling.
- The discovery highlights the hidden role fungi play in maintaining Himalayan forest ecosystems.
Why India’s Fungal Diversity Matters
- India’s fungal biodiversity remains vastly underexplored, especially in high-altitude and temperate forests.
- Discoveries like Hemileccinum indicum suggest that many species remain undocumented.
- Fungi are critical for ecosystem balance, climate resilience, and even future pharmaceutical research.
- Protecting forest habitats is therefore essential not only for visible wildlife but also for microscopic life that sustains entire ecosystems.
Question
Q. Hemileccinum indicum was discovered in which type of forest ecosystem?
A. Mangrove forests
B. Tropical rainforests
C. Temperate oak forests
D. Alpine grasslands



 Kerala Officially Adopts Bacillus subtil...
Kerala Officially Adopts Bacillus subtil...
 IIT Guwahati Creates Technique to Track ...
IIT Guwahati Creates Technique to Track ...
 Microsoft Unveils Maia 200 AI Chip, Chal...
Microsoft Unveils Maia 200 AI Chip, Chal...







