
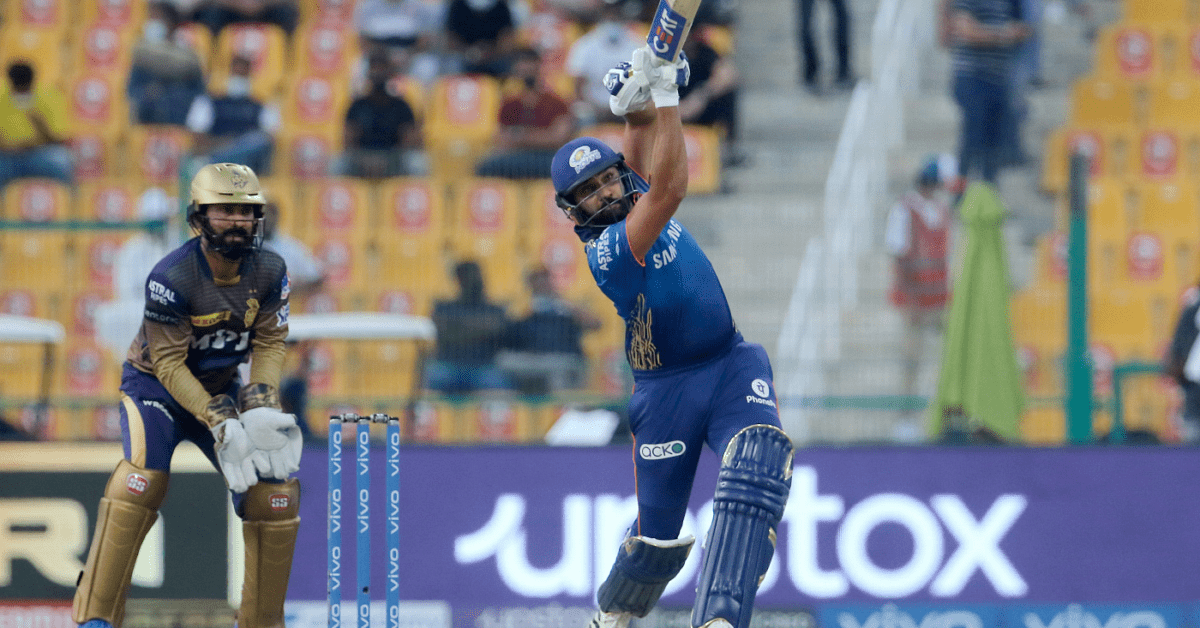
Rohit Sharma became the first batter in the Indian Premier League (IPL) history to score 1000 runs against a single team during Mumbai Indians’ (MI) contest against Kolkata Knight Riders (KKR) at the Sheikh Zayed Stadium, Abu Dhabi. The 34-year-old achieved the feat in the fourth over of MI’s innings. Rohit now has 1015 runs against KKR at an average of 46.13 and a strike rate of 132.16, including six fifties and one hundred.
Buy Prime Test Series for all Banking, SSC, Insurance & other exams



 India Beat Pakistan in T20 World Cup 202...
India Beat Pakistan in T20 World Cup 202...
 Weekly One Liners 09th to 15th of Februa...
Weekly One Liners 09th to 15th of Februa...
 Highest Partnerships in India–Pakistan T...
Highest Partnerships in India–Pakistan T...








