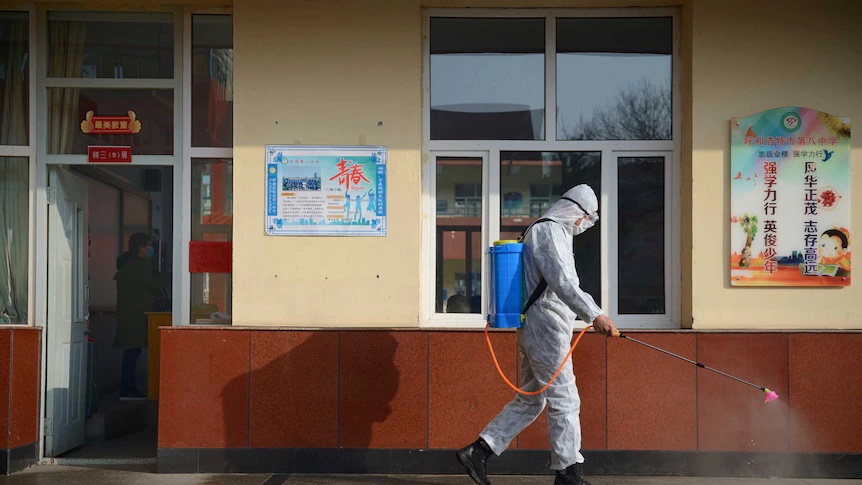
China’s Inner Mongolia region has reported two cases of bubonic plague, causing concerns amid previous infections and highlighting the need for vigilant containment efforts. The new cases involve close relatives of a previously infected individual. Bubonic plague is a highly infectious disease, primarily transmitted through rodents, and can be fatal if not treated promptly. The region’s health authorities are taking proactive measures to prevent the further spread of the disease.
Continued Vigilance Amidst New Cases
Following a prior bubonic plague infection detected on August 7, China’s northern region of Inner Mongolia has once again encountered two cases of the disease. These new cases involve the husband and daughter of the previous infected person, as confirmed by the local government’s official statement.
Swift Quarantine Measures and Absence of Abnormal Symptoms
To curb the potential spread of the disease, authorities have taken swift action by quarantining all close contacts of the newly infected individuals. It is reassuring to note that as of now, none of the quarantined contacts have exhibited any abnormal symptoms related to bubonic plague. This proactive approach emphasizes the region’s commitment to preventing a wider outbreak.
Bubonic Plague: A Persistent but Limited Threat
China has experienced relatively low numbers of bubonic plague cases in recent years, with most instances reported in the Inner Mongolia and northwestern Ningxia regions. The disease is primarily spread by rodents, making these areas conducive to its transmission. The World Health Organization (WHO) underscores that bubonic plague is the most common form of plague and can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Upholding Public Health: WHO’s Perspective
The World Health Organization emphasizes the critical importance of swift and effective treatment when dealing with bubonic plague. The disease’s potential fatality underscores the need for prompt medical intervention. WHO’s guidance serves as a reminder for health authorities and medical professionals to remain vigilant and prepared in managing potential outbreaks.
Find More International News Here




 States and Capitals - How Many States in...
States and Capitals - How Many States in...
 Leopard 2A7 vs Challenger 3: Best NATO M...
Leopard 2A7 vs Challenger 3: Best NATO M...
 Kaziranga Ranks Third Globally in Tiger ...
Kaziranga Ranks Third Globally in Tiger ...

