Index of Economic Freedom
The Index of Economic Freedom is an annual report that measures the level of economic freedom in countries around the world. The index is published by The Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank based in Washington D.C., in partnership with The Wall Street Journal. The index uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative data to rank countries on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 representing the highest level of economic freedom.
Buy Prime Test Series for all Banking, SSC, Insurance & other exams
Index of Economic Freedom: Overview
Below is the overview of Index of Economic Freedom:
Index of Economic Freedom: Overview |
|
| Name of the Index | Index of Economic Freedom |
| Published by | The Heritage Foundation |
| Headquarters of Publisher | Washington D.C |
| Partners in Publishing | Wall Street Journal |
| Rating Scale | 0 to 100 |
Index of Economic Freedom: Methodology
The index is based on four main pillars of economic freedom: rule of law, government size, regulatory efficiency, and open markets. Within these pillars, the index measures factors such as property rights, government spending, business freedom, labor freedom, and trade freedom. Each of these factors is given a score, and the scores are combined to create an overall score for each country.
The Index of Economic Freedom follows a methodology that is categorized into four groups, each consisting of 12 aspects. These are:
-
Rule of Law
a. Property Rights: This evaluates a country’s capacity to legally safeguard the property rights of its citizens.
b. Judicial Effectiveness: This measures the effectiveness and impartiality of the judiciary in relation to property laws.
c. Government Integrity: This assesses the strength of the government and the occurrence of corrupt practices such as bribery, nepotism, patronage, embezzlement, cronyism, and graft.
-
Government Size
a. Tax Burden: This examines the percentage of personal and corporate income that is subject to marginal tax rates and overall taxation levels, including indirect and direct taxes, as a proportion of the GDP.
b. Government Spending: This analyzes the quantity of government spending and its related burden, including state consumption and transfer payments for various entitlement programs.
c. Fiscal Health: This assesses a country’s ability to manage its budgets by measuring growing debt and deficit.
-
Efficiency of Regulation
a. Business Freedom: Assesses the cost, time, and degree of freedom associated with starting, operating, and shutting down a business, considering factors like electricity costs.
b. Labor Freedom: Measures the level of interference in labor rights, including minimum wage laws, restrictions on layoffs, severance pay requirements, and regulatory constraints on hiring and working hours, as well as the labor force participation rate.
c. Monetary Freedom: Examines the stability of prices and the extent to which the microeconomy is regulated.
-
Openness of Markets
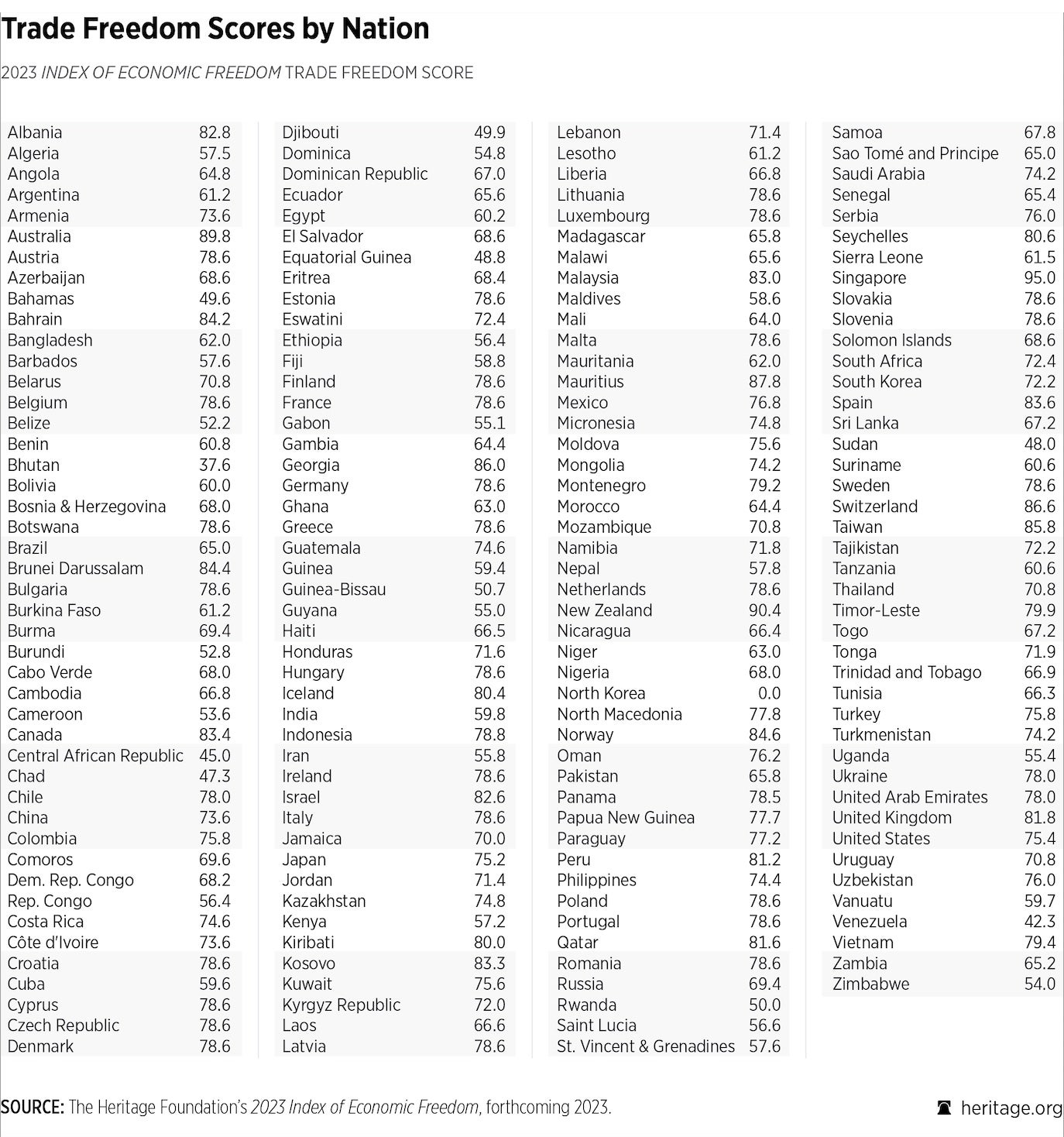
a. Trade Freedom: Measures the impact of tariff and non-tariff barriers on the import and export of goods and services in and out of the country.
b. Investment Freedom: Evaluates the degree of freedom or restrictions on the movement of investment capital for individuals and firms.
c. Financial Freedom: Indicates the efficiency of the banking system and the level of independence of the government from the financial sector.
Index of Economic Freedom: Key Features
- The index is widely used by governments, businesses, and investors to assess the economic climate in different countries.
- A higher score on the index is seen as an indicator of a more attractive investment climate, while a lower score can be a warning sign of potential economic problems.
- According to the 2021 Index of Economic Freedom, Hong Kong topped the rankings for the 27th consecutive year, followed by Singapore, New Zealand, Australia, and Switzerland.
- The United States ranked 20th, while China ranked 107th out of 180 countries.
- The index also highlighted the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global economic freedom, with many countries experiencing declines in economic freedom due to increased government intervention in response to the pandemic.
- Critics of the index argue that it reflects a conservative bias, as it tends to favor countries with low taxes and minimal government intervention in the economy.
- They also note that the index does not take into account social or environmental factors, and may therefore provide an incomplete picture of a country’s overall economic health.
Despite these criticisms, the Index of Economic Freedom remains a widely used tool for assessing economic conditions around the world. Its focus on key economic indicators and its comprehensive coverage of a wide range of countries make it a valuable resource for investors, policymakers, and business leaders. As the global economy continues to evolve, the index will likely continue to play an important role in shaping economic policy and investment decisions.
Index of Economic Freedom: Rank of India
Currently, India is categorized as “Mostly Unfree” in terms of the economic freedom its inhabitants enjoy. The 2023 Index of Economic Freedom gave India a total score of 59.8 out of 100, which translates to a 59.8% performance on the index. India’s total score on the 2023 Index is its lowest in six years. In the Index, India is placed at the 121st spot out of 184 nations. India still struggles in areas such as government honesty, freedom for labor, and financial stability, which are significant factors that impact its total score and position on the Index.
Index of Economic Freedom: Top 10 Countries
Below is the rank of Top 10 Countries in the Index of Economic Freedom:
Top 10 Countries in the Index of Economic Freedom |
||
| Rank | Country Name | Score |
| 1 | Singapore | 89.7 |
| 2 | New Zealand | 83.9 |
| 3 | Australia | 82.4 |
| 4 | Switzerland | 81.9 |
| 5 | Ireland | 81.4 |
| 6 | Taiwan | 78.6 |
| 7 | United Kingdom | 78.4 |
| 8 | Estonia | 78.2 |
| 9 | Canada | 77.9 |
| 10 | Denmark | 77.8 |
Index of Economic Freedom: SAARC Countries
Below is the rank of SAARC Countries in the Index of Economic Freedom:
SAARC Countries in the Index of Economic Freedom |
||
| Rank | Country Name | Score |
| 109 | Bhutan | 58.3 |
| 121 | Bangladesh | 55.6 |
| 121 | India | 59.8 |
| 131 | Sri Lanka | 55.7 |
| 146 | Afghanistan | 53.0 |
| 152 | Pakistan | 51.7 |
| 157 | Nepal | 50.7 |
Index of Economic Freedom: List by The Heritage Foundation
Below is the list published by the Heritage Foundation of the Index of Economic Freedom:
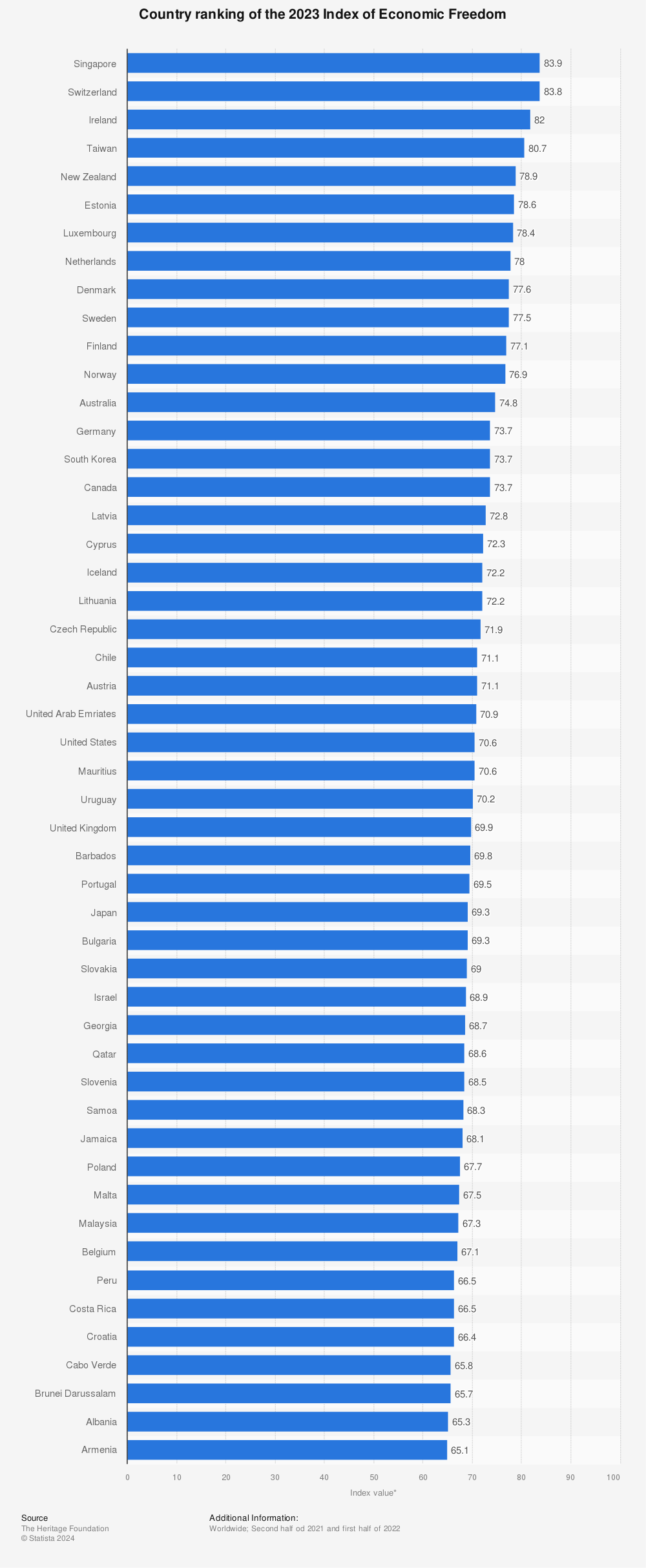
Scores of Index of Economic Freedom by The Heritage Foundation
Below is the Scores of the Index of Economic Freedom published by the Heritage Foundation :
Index of Economic Freedom: Significance
- The index has become an important tool for policymakers, economists, and investors around the world who are interested in understanding the relationship between economic freedom and economic growth.
- Countries with high scores on the index are generally seen as more attractive to foreign investment, and are often cited as models of successful economic development.
- One of the key benefits of the Index of Economic Freedom is that it provides a clear, objective measure of economic freedom that can be used to compare different countries and regions.
- This allows policymakers and investors to identify areas where improvements in economic freedom could be made, and to target resources accordingly.
- For example, if a country scores low on the index in the area of property rights, policymakers might focus on strengthening property rights laws and regulations in order to attract more investment and encourage economic growth.
- Similarly, if a country scores low on the index in the area of government spending, policymakers might focus on reducing government spending in order to create a more favorable economic environment for businesses and individuals.
India Ranks Fourth in Global Military Expenditure: SIPRI Report
Index of Economic Freedom: Importance
- The index is also useful for identifying trends in economic freedom over time.
- By comparing scores from one year to the next, policymakers and investors can see whether a country is moving in the right direction in terms of economic freedom, or whether it is stagnating or even regressing.
- This can help them to make informed decisions about where to invest their resources, and which countries are most likely to experience economic growth in the future.
- In addition to its practical applications, the Index of Economic Freedom also has important theoretical significance.
- It is based on the idea that economic freedom is a fundamental human right, and that societies that protect and promote economic freedom are more likely to prosper and flourish over the long term.
- This idea is supported by a wealth of empirical evidence, which shows that countries with higher levels of economic freedom tend to have higher levels of economic growth, greater innovation and entrepreneurship, and higher levels of prosperity and well-being for their citizens.
- In conclusion, the Index of Economic Freedom is a valuable tool for policymakers, economists, and investors who are interested in promoting economic growth and development around the world.
- By measuring the degree of economic freedom in different countries and regions, the index allows us to identify areas where improvements could be made, and to target resources accordingly.
- It also provides a clear, objective measure of economic freedom that can be used to compare different countries and regions, and to identify trends over time.
- Ultimately, the index helps to promote the idea that economic freedom is a fundamental human right, and that societies that protect and promote economic freedom are more likely to prosper and flourish over the long term.
Also Read: Freedom House Index: Tibet ranked the world’s least free country
Find More Ranks and Reports Here

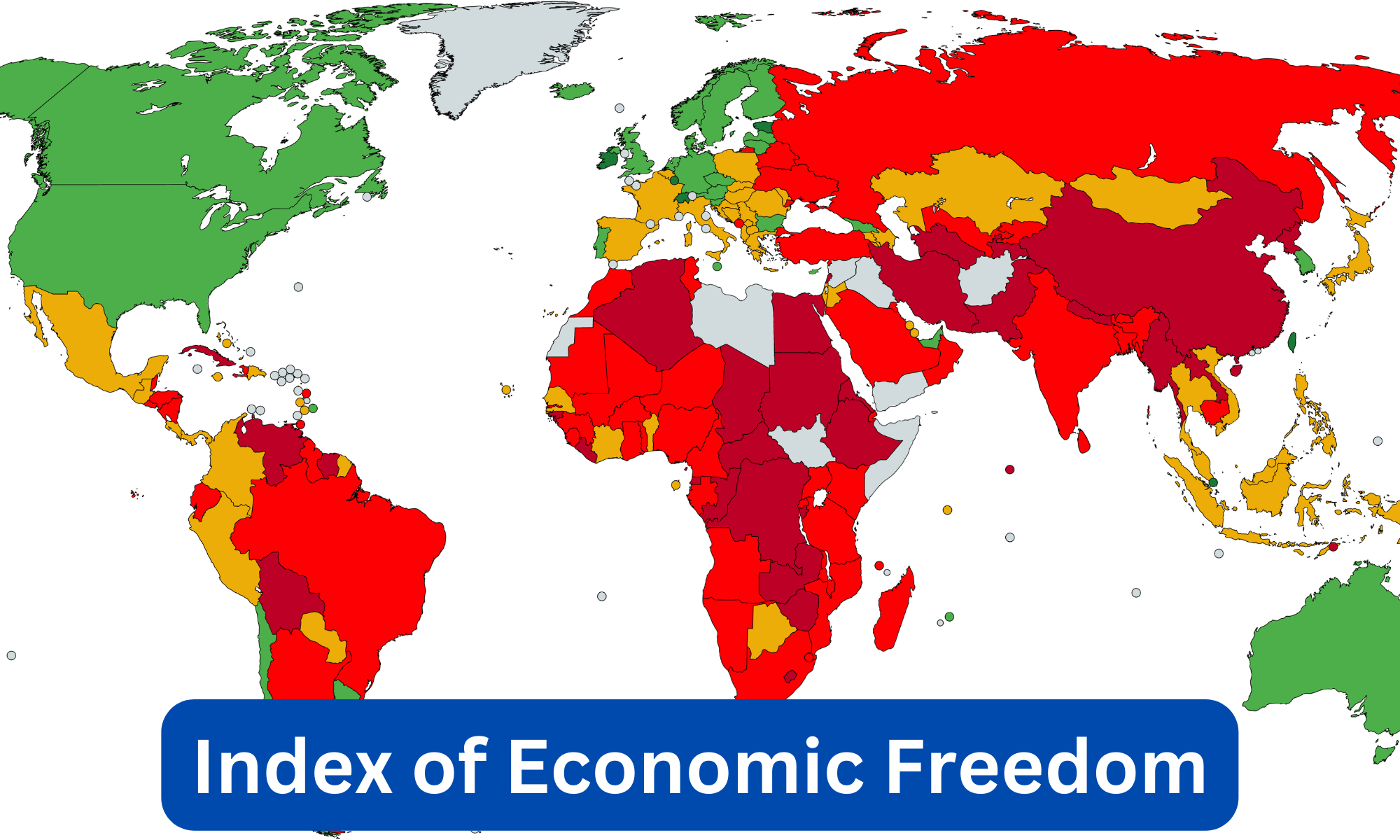

 Which Place is known as the Diamond Capi...
Which Place is known as the Diamond Capi...
 List of Major LPG Gas Companies in India...
List of Major LPG Gas Companies in India...
 WHO Foundation and Novo Nordisk Launch I...
WHO Foundation and Novo Nordisk Launch I...








