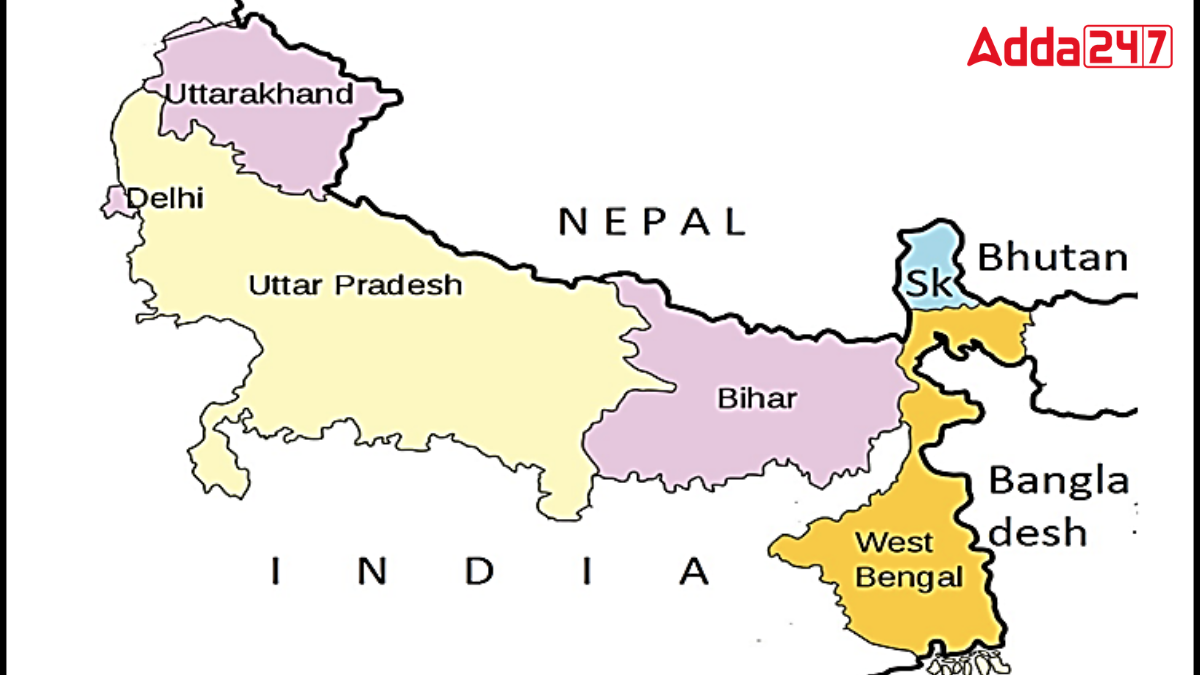
India shares its borders with several countries, including China, Nepal, Myanmar (Burma), Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Bhutan. In terms of area, India is the seventh largest country in the world. This article will provide detailed information about the Indian states that share a border with Nepal.
Historical Background
The border between India and Nepal was established after the Treaty of Sugauli in 1816 between Nepal and the British Raj. After India gained independence from British rule on August 15, 1947, the border took its current form. In 1950, the India-Nepal Peace and Friendship Treaty was signed.
States Sharing Border with Nepal
Here is the approximate length of the border that each state shares with Nepal:
- Uttar Pradesh: 551 km
- Uttarakhand: 275 km
- West Bengal: 100 km
- Bihar: 726 km
- Sikkim: 99 km
- Total: 1,751 km
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is the fourth largest state in India, located in the north-central part of the country.
- North: Bordered by Nepal.
- East: Bordered by Bihar.
- Southeast: Bordered by Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh.
- South: Bordered by Madhya Pradesh.
- West: Bordered by Rajasthan, Haryana, and the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
Uttar Pradesh was named on January 26, 1950, when India became a republic. Its capital is Lucknow, with an area of 240,928 sq km and a population of 199,812,341 as per the 2011 census. The state is divided into two regions: the southern hills and the plains of the Ganges. Agriculture is the main occupation, with 66% of the population engaged in farming.
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand became the 27th state of India on November 9, 2000.
- North: Bordered by China (Tibet).
- East: Bordered by Nepal.
- Northwest: Bordered by Himachal Pradesh.
- South: Bordered by Uttar Pradesh.
Located in the foothills of the Himalayan mountain range, Uttarakhand is a large mountainous state with an area of 53,483 sq km and a population of 10,116,752 as per the 2011 census. The capital is Dehradun. The state bird is the Himalayan Monal, the state tree is Rhododendron (Buransh), and the state flower is Brahma Kamal. The spoken languages are Hindi, Garhwali, and Kumaoni.
West Bengal
West Bengal is located in the eastern part of India.
- North: Bordered by Bhutan and Sikkim.
- East: Bordered by Bangladesh.
- Northeast: Bordered by Assam.
- South: Bordered by the Bay of Bengal.
- Northwest: Bordered by Nepal.
- West: Bordered by Bihar.
West Bengal was formed on January 26, 1950. It covers an area of 88,752 sq km and has a population of 91,347,736 as per the 2011 census. The capital is Kolkata. The languages spoken are Bengali, Hindi, English, and Nepali. The state animal is the fishing cat, the state bird is the white-throated kingfisher, the state tree is the devil tree, and the state flower is night-flowering jasmine.
Bihar
Bihar is located in the eastern part of India and is a landlocked state.
- North: Bordered by Nepal.
- Northeast: Bordered by West Bengal.
- South and Southeast: Bordered by Jharkhand.
The capital of Bihar is Patna. The state covers an area of 94,163 sq km and has a population of 103,804,637 as per the 2011 census. The main languages spoken are Hindi, Urdu, Bihari, Bhojpuri, Maithili, and Magahi. Approximately three-quarters of the population depends on agriculture.
Sikkim
Sikkim is located in the northeastern part of India and is one of the smallest states.
- North and Northeast: Bordered by China (Tibet Autonomous Region).
- Southeast: Bordered by Bhutan.
- South: Bordered by West Bengal.
- West: Bordered by Nepal.
The capital of Sikkim is Gangtok. The state has an area of 7,096 sq km and a population of 607,688 as per the 2011 census. The major tribal groups are Bhutia, Lepcha, and Limbu, who speak Tibeto-Burman languages and follow Mahayana Buddhism along with the indigenous Bon religion.



 Which Lake is known as the Jewel of Udai...
Which Lake is known as the Jewel of Udai...
 Which is the Largest Banana Producing St...
Which is the Largest Banana Producing St...
 Which is the First Tiger Reserve of Utta...
Which is the First Tiger Reserve of Utta...








