The Sustainable Trade Index 2024, jointly published by the Hinrich Foundation and IMD, highlights the global shift toward sustainability in trade. As the world recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic, nations are focusing on resilience to combat potential future crises such as climate change, geopolitical tensions, and economic instability. The Sustainable Trade Index evaluates economies based on three critical pillars:
- Economic Growth
- Societal Advancement
- Environmental Resilience
This index emphasizes the importance of balancing economic, social, and environmental factors in trade practices to ensure sustainable and inclusive growth.
Defining Sustainable Trade
Sustainable trade involves mutually beneficial outcomes for trading partners while maintaining a balance between:
- Economic stability
- Social progress
- Environmental conservation
Global economies are increasingly adopting policies to strengthen domestic industries, build a resilient workforce, and integrate trade with environmental goals. By addressing these dimensions, economies can establish robust systems that withstand shocks and promote green development.
Top 10 Most Sustainable Trade Economies in 2024
| Rank | Economy | Overall Score | Economic | Societal | Environmental | Key Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Zealand | 100 | 86 | 100 | 100 | Tops all three pillars; retained the top position for the third consecutive time. |
| 2 | United Kingdom | 97.7 | 87.8 | 93.7 | 99.4 | Strong in environmental resilience and societal progress; slight dip in economic. |
| 3 | Australia | 87.4 | 75.4 | 99.6 | 83.2 | Excels in societal and environmental dimensions. |
| 4 | Singapore | 85.7 | 92.4 | 87 | 75.2 | Leads in economic growth while maintaining societal and environmental strengths. |
| 5 | Japan | 81.5 | 72.2 | 81.9 | 91.2 | Highly resilient in environmental factors despite societal and economic challenges. |
| 6 | South Korea | 81.4 | 92.2 | 85.4 | 67.4 | Strong in economic and societal pillars; faces environmental challenges. |
| 7 | Hong Kong | 81.4 | 100 | 65.8 | 79.2 | Dominates in the economic pillar but lags in societal progress. |
| 8 | Canada | 80 | 81.1 | 99.8 | 61 | Excels in societal factors; environmental scores indicate room for improvement. |
| 9 | Taiwan | 72.3 | 76.7 | 87.1 | 61.2 | Balances economic and societal dimensions; faces environmental challenges. |
| 10 | United States of America | 72.2 | 90 | 69.4 | 65.3 | Strong economic growth; moderate societal and environmental resilience. |
India’s Performance: A Detailed Analysis
India’s Overall Rank: 23rd Globally
Despite being the fifth-largest economy in the world, India’s performance in the Sustainable Trade Index highlights significant economic strengths but also reveals critical challenges in societal and environmental dimensions.
India’s Scores Across Pillars:
- Economic Factors: 62.3
- Societal Aspects: 13.3
- Environmental Considerations: 43.1
Economic Performance: A Strong Foundation
India’s economic score of 62.3 showcases its rapid economic growth and the implementation of pro-growth policies. Key drivers include:
- A booming industrial sector.
- Expanding global trade partnerships.
- Efforts to strengthen domestic manufacturing through initiatives like ‘Make in India’.
However, economic inequalities persist, limiting India’s ability to create an equitable workforce and reduce disparities.
Societal Challenges: A Need for Reform
With a score of 13.3, India’s societal performance reflects significant areas of concern, including:
- Poverty: Despite progress, millions still live below the poverty line.
- Gender Inequality: Women face barriers in accessing education, employment, and financial independence.
- Healthcare Access: Unequal access to healthcare facilities continues to be a challenge.
Investments in education, social infrastructure, and gender equality are crucial to improve India’s societal standing.
Environmental Factors: A Mixed Bag
India’s environmental score of 43.1 highlights both progress and persistent issues:
Strengths:
- Adoption of renewable energy solutions, including solar and wind power.
- Participation in international agreements like the Paris Accord.
Challenges:
- Severe air pollution, especially in urban areas.
Deforestation and loss of biodiversity.
- Limited progress in waste management and water conservation.
To enhance environmental sustainability, India must adopt stricter policies to curb pollution and promote sustainable practices.
Global Implications of India’s Position
India’s rank highlights its pivotal role in the global economy and its potential to drive sustainable trade practices. However, the low scores in societal and environmental pillars emphasize the need for:
- Comprehensive policies addressing social inequalities.
- Aggressive measures to tackle climate change and pollution.
- Enhanced collaboration with global partners to adopt best practices in sustainability.
Summary of News: Sustainable Trade Index 2024
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Why in News | The Sustainable Trade Index 2024, published by Hinrich Foundation and IMD, ranks India 23rd globally, highlighting its strengths and challenges in sustainable trade. |
| Key Report | The index evaluates economies based on three pillars: Economic Growth, Societal Advancement, and Environmental Resilience. |
| Top Performers | – 1st: New Zealand (Score: 100, tops all pillars). |
| – 2nd: United Kingdom (Score: 97.7, strong societal and environmental performance). | |
| – 3rd: Australia (Score: 87.4, excels in societal and environmental factors). | |
| India’s Rank | 23rd globally in the Sustainable Trade Index 2024. |
| India’s Scores | – Overall Score: 24 |
| – Economic Factors: 62.3 | |
| – Societal Aspects: 13.3 | |
| – Environmental Factors: 43.1 | |
| Economic Strengths | – Strong economic growth supported by initiatives like ‘Make in India’. |
| – Booming industrial sector and expanding global trade partnerships. | |
| Societal Challenges | – Poverty: Millions still live below the poverty line. |
| – Gender Inequality: Women face barriers in education, employment, and financial independence. | |
| – Healthcare Access: Unequal access to healthcare facilities persists. | |
| Environmental Issues | – Strengths: Adoption of renewable energy solutions, active participation in global agreements. |
| – Challenges: Severe air pollution, deforestation, poor waste management, and water conservation. | |
| Global Implications | India’s performance highlights its pivotal role in sustainable trade but underscores the need for: |
| – Policies addressing societal inequalities. | |
| – Aggressive environmental measures to combat pollution. | |
| – Collaboration with global partners to adopt sustainability best practices. |



 Top 10 Richest People in the World 2026:...
Top 10 Richest People in the World 2026:...
 Top 10 Most Popular Websites of 2026: Go...
Top 10 Most Popular Websites of 2026: Go...
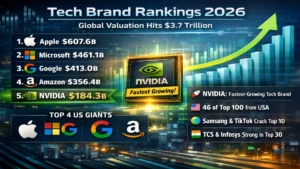 Top 10 Most Valuable Technology Brands i...
Top 10 Most Valuable Technology Brands i...








