Haryana, a state in northern India, is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, vibrant history, and rapid urban development. Amidst its varied landscapes and diverse districts, one stands out for its sheer expanse and significance: Sirsa. Let’s delve into the heart of Haryana’s largest district and uncover its unique features and contributions to the state’s tapestry.
How Many Districts are there in Haryana?
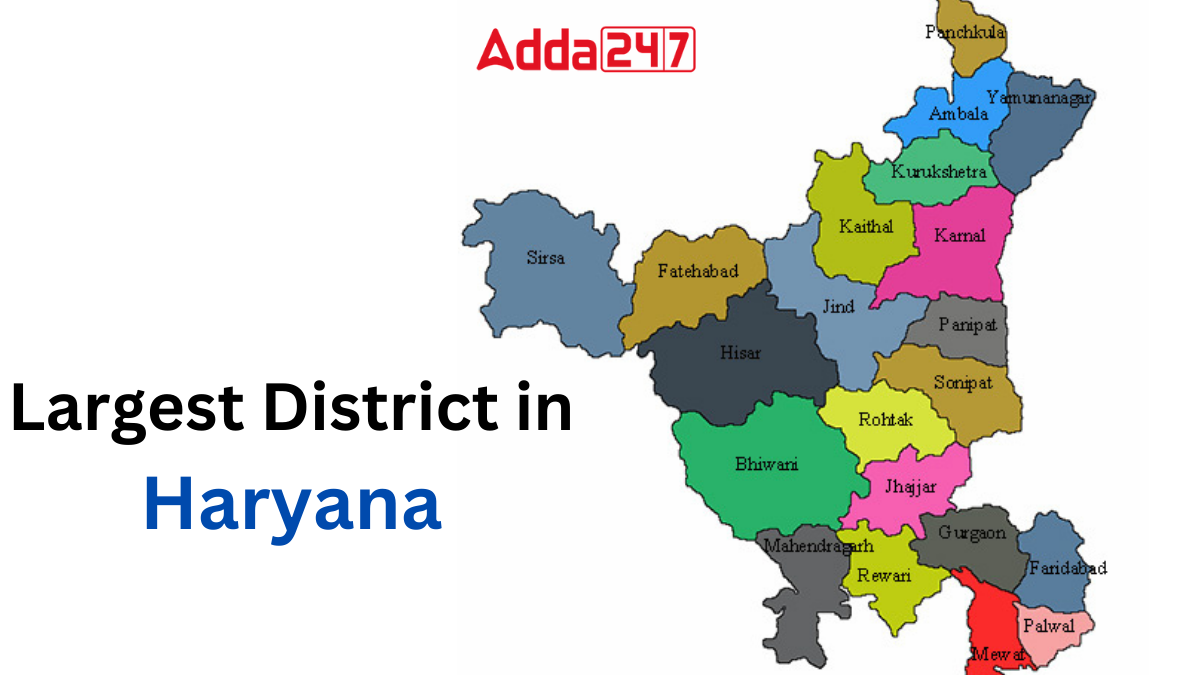
Haryana, initially comprised of 7 districts, has seen significant expansion over the years. Presently, the state boasts a total of 22 districts. The most recent addition to Haryana’s district roster occurred in 2016 with the formation of Charkhi Dadri district.
Largest District in Haryana
Sirsa, the largest district of Haryana, is known for its cultural richness, economic growth, and historical importance. Created in 1975, the district lies on National Highway 9, about 250 km from Delhi, making it an important link for trade and travel. Agriculture is the backbone of Sirsa’s economy, supported by industries and commerce. With its wide area, diverse communities, and active role in administration, Sirsa stands out as a key part of Haryana’s social and economic development.
Key Facts About Biggest District in Haryana
Here are some key facts related to Sirsa, the largest district of Haryana:
- Sirsa District is the largest district in Haryana by area, encompassing approximately 4,277 square kilometers.
- Established on September 1, 1975, Sirsa became a district by incorporating Sirsa and Dabwali tahsils from Hisar District.
- The district headquarters, Sirsa, is situated along National Highway 9, about 250 kilometers from the capital city of Delhi.
- Sirsa District comprises a total of 342 villages, showcasing its extensive rural landscape and population dispersion.
- In 2006, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj identified Sirsa as one of India’s 250 most backward districts, emphasizing its developmental challenges.
- As per the 2011 census, Sirsa District recorded a population of 1,295,189 individuals, with a population density of 303 inhabitants per square kilometer.
- The religious demography of Sirsa District reflects a majority Hindu population, followed by Sikhism, Islam, and other faiths.
- The linguistic diversity in Sirsa includes languages such as Punjabi, Bagri, Hindi, and Haryanvi, with Punjabi being the most widely spoken after Hindi.
- Notable personalities hailing from Sirsa District include cricketer Barinder Sran, politician Devi Lal, and singer-composer Gajendra Verma, among others.
- Sirsa District has made significant contributions to various fields, including sports, politics, entertainment, and literature, enriching Haryana’s cultural landscape.
Largest District of Haryana in terms of Population
Faridabad District holds the distinction of being the most populous district in Haryana, with a population of 18 lakhs as per the 2011 census. Its significant population makes it the largest district in Haryana in terms of demographic density. Situated in the National Capital Region (NCR), Faridabad District encompasses a diverse array of communities and contributes significantly to the socio-economic fabric of the state.
Districts of Faridabad, Name list
Below is a list containing the names of all 22 districts in Haryana, encompassing both the older established districts and the newly formed ones. This table provides a comprehensive overview of the district composition within the state of Haryana.
| Districts of Faridabad, Name List | |
| Ambala | Charkha Dadri |
| Fatehabad | Hisar |
| Jind | Karnal |
| Mahendragarh | Palwal |
| Panipat | Rohtak |
| Sonipat | Bhiwani |
| Faridabad | Gurugram |
| Jhajjar | Kaithal |
| Kuruskhetra | Nuh |
| Panchkula | Rewari |
| Sirsa | Yamunanagar |



 Which River is known as the Black River?...
Which River is known as the Black River?...
 Which State is the Largest Producer of C...
Which State is the Largest Producer of C...
 Which State is the Largest Producer of J...
Which State is the Largest Producer of J...








