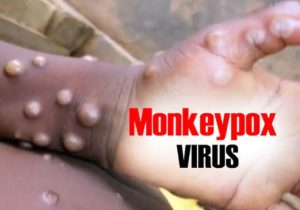
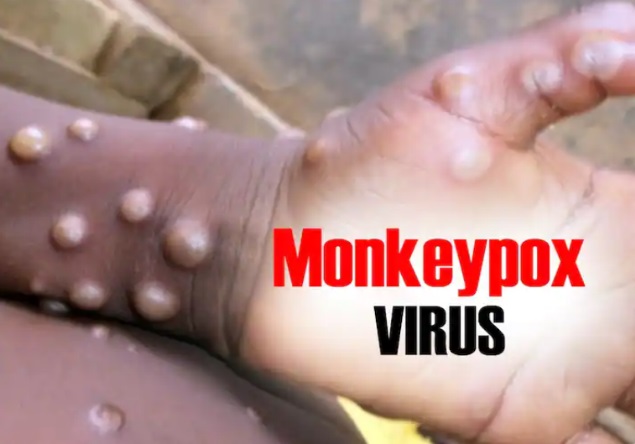
The first case of monkeypox was confirmed in India after a person who had returned to Kerala from UAE developed symptoms of the disease. His samples were sent to National Virology Institute in Pune which confirmed the disease. It was first found in monkeys in 1958.
According to the WHO, monkeypox is a viral zoonosis (a virus transmitted to humans from animals) with symptoms similar to those seen in the past in smallpox patients, although it is clinically less severe. It is usually a self-limited disease with symptoms lasting two to four weeks.
About Monkeypox:
- Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic disease with symptoms similar to smallpox, although with less clinical severity. The virus is transmitted through close contact with another infected person or animal and spreads from lesions, body fluids, respiratory droplets and contaminated materials such as bedding.
- The symptoms can include fever, headache, muscle ache and backache, swollen lymph nodes, chills, exhaustion, and rashes that can look like pimples or blisters on the face, inside the mouth and other parts of the body.
- As infection turns acute, red lesions will appear on the body and the itching-like chicken pox is triggered. The incubation period ranges from five to 21 days.



 Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Kham...
Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Kham...
 Which Country Officially Uses Two Differ...
Which Country Officially Uses Two Differ...
 Historic Glory! Jammu & Kashmir Win ...
Historic Glory! Jammu & Kashmir Win ...








