India’s rural employment policy has entered a new phase with the Viksit Bharat–Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) – VB–G RAM G 2025. Touted as the biggest reform since MNREGA (2005), the new law shifts the focus from short-term wage relief to asset-based, productivity-driven rural development.
For government job aspirants and general readers, a clear tabular comparison helps in quickly understanding how VB–G RAM G differs from MNREGA in objectives, structure, funding, and impact.
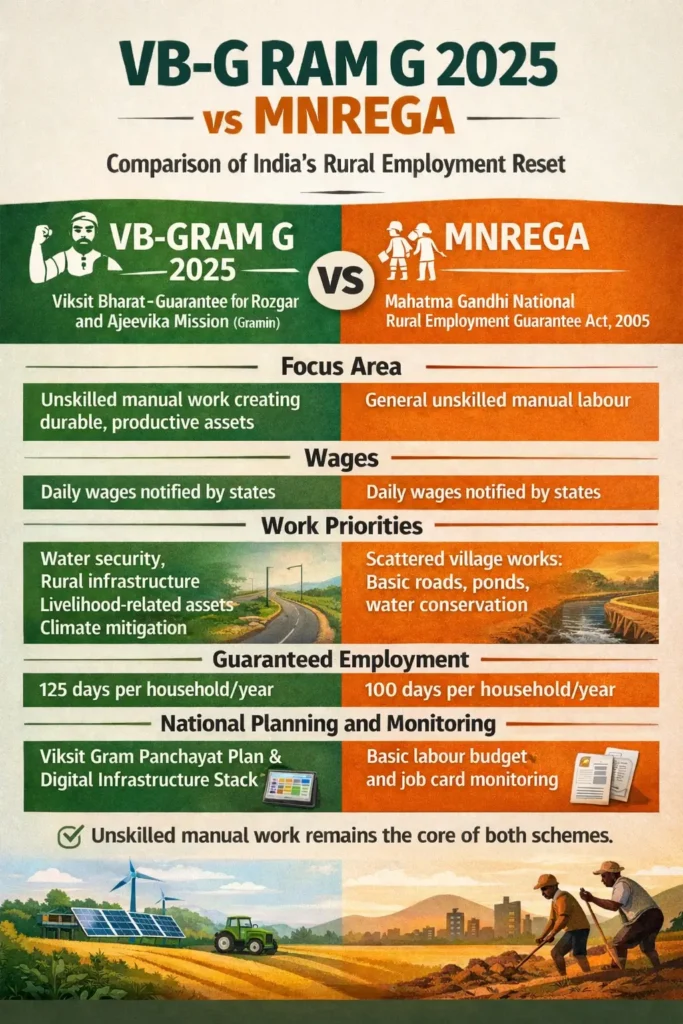
VB–G RAM G 2025 vs MNREGA: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Parameter | MNREGA (2005) | VB–G RAM G 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Status | Statutory right to work under MGNREGA Act | Statutory guarantee retained under new law |
| Guaranteed Employment | 100 days per rural household per year | 125 days per rural household per year |
| Nature of Work | Unskilled manual work | Unskilled manual work with asset focus |
| Core Objective | Short-term income support | Income security + productivity + livelihoods |
| Approach to Employment | Demand-driven wage employment | Employment linked to durable asset creation |
| Work Categories | Broad, scattered list of permissible works | 4 focused work verticals |
| Primary Development Focus | Social protection | Rural infrastructure and economic resilience |
Comparison of Work Structure and Planning
| Aspect | MNREGA | VB–G RAM G 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Work Planning | Annual labour budget, often ad-hoc | Viksit Gram Panchayat Plan |
| Asset Selection | Panchayat-driven, flexible | Strategically mapped and prioritised |
| Integration with National Plans | Limited integration | Linked with PM Gati-Shakti and national platforms |
| Spatial Mapping | Minimal | Mandatory digital and GIS mapping |
| Asset Durability | Often short-lived | Focus on long-term, productive assets |
Work Priorities: Then vs Now
| Dimension | MNREGA | VB–G RAM G 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Water-Related Works | One of many categories | Top priority vertical |
| Rural Infrastructure | Limited and fragmented | Roads, storage, connectivity to markets |
| Livelihood Assets | Indirect impact | Direct support to agriculture and enterprises |
| Climate Resilience | Not central | Core pillar of the scheme |
| Disaster Mitigation | Sporadic | Flood control, soil conservation prioritised |
Digital and Governance Framework
| Feature | MNREGA | VB–G RAM G 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Tracking | MIS-based reporting | National Rural Infrastructure Stack |
| Asset Database | Fragmented | Unified national digital platform |
| Transparency Tools | Social audits, job cards | Digital planning + mapped assets |
| Monitoring | Post-facto checks | Real-time integration across levels |
| Leakage Control | Mixed results | Designed to reduce duplication and misuse |
Funding Model Comparison
| Aspect | MNREGA | VB–G RAM G 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Budgeting Method | Demand-driven, open-ended | Normative funding |
| Employment Guarantee | Yes | Yes (legally protected) |
| Unemployment Allowance | Mandatory if work not given | Mandatory if work denied |
| Budget Predictability | Often uncertain | Higher predictability |
| Criticism | Delayed payments, fund misuse | Risk of de facto caps debated |
Centre–State Cost Sharing
| Region | MNREGA | VB–G RAM G 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| General States | 60:40 | 60:40 |
| NE & Himalayan States | 90:10 | 90:10 |
| UTs (No Legislature) | 100% Centre | 100% Centre |
Impact on Farmers and Labourers
| Stakeholder | MNREGA Impact | VB–G RAM G 2025 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Farmers | Labour shortages during peak seasons | States can pause works for up to 60 days |
| Agricultural Costs | Wage distortions reported | More stable labour availability |
| Labourers | Unpredictable work availability | Predictable schedules, higher days |
| Migration | Limited reduction | Expected decline in distress migration |
| Long-Term Benefits | Mostly wage-based | Wage + infrastructure + livelihoods |



 Delhi to Implement ‘Rah-Veer’ Scheme to ...
Delhi to Implement ‘Rah-Veer’ Scheme to ...
 2 Years of PM Surya Ghar Scheme: Rooftop...
2 Years of PM Surya Ghar Scheme: Rooftop...
 From Seva Teerth, PM Modi Announces PM R...
From Seva Teerth, PM Modi Announces PM R...








