India has cemented its position as the third-largest digitalized nation in the world, trailing only behind the technological powerhouses of the United States of America (USA) and China. This significant finding is part of the “State of India’s Digital Economy Report, 2024,” unveiled by the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER), a renowned Delhi-based think tank. The report paints a comprehensive picture of India’s digital landscape, comparing it favorably with some of the world’s most developed economies, yet highlighting areas for improvement in user-level digital engagement.
A Comprehensive Analysis: The ‘CHIPS’ Framework
ICRIER’s study employs the innovative ‘CHIPS’ framework to evaluate the digital prowess of nations across five critical dimensions: connect, harness, innovate, protect, and sustain. This methodology offers a holistic view of the digital ecosystem, allowing for a nuanced understanding of India’s digital economy relative to global standards.
India’s Global Digital Standing
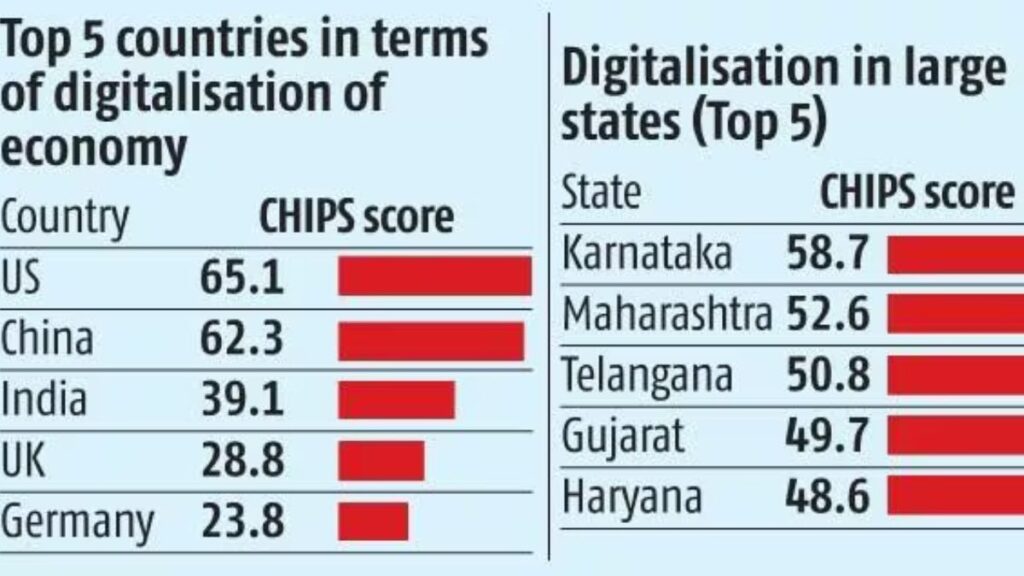
The report’s findings underscore India’s formidable presence on the digital stage. Surpassing developed nations like the United Kingdom, Germany, and Japan in aggregate levels of digitalization, India has showcased its ability to leverage digital technology for economic and social advancement. However, the country’s rank as the 12th in terms of individual user digitalization among G20 nations points to a disparity between overall digital infrastructure and the personal digital engagement of its citizens.
The Significance of Digital Infrastructure
India’s digital infrastructure has been a key driver of its third-place ranking. Investments in connectivity, digital services, and technology innovation have paid dividends, positioning the country as a significant player in the global digital economy. The government’s focus on digital initiatives, such as the Digital India campaign, has been instrumental in this growth, expanding digital access and literacy across diverse demographics.
Bridging the User Engagement Gap
While India’s digital infrastructure sets a global benchmark, the report highlights a crucial gap in individual digital engagement. Ranking 12th among G20 countries in this aspect indicates room for improvement in making digital advancements more inclusive and accessible to all segments of the population. Efforts to enhance digital literacy, affordability, and usability can bridge this gap, ensuring that the benefits of digitalization are equitably distributed.




 India's Progress in Human Development In...
India's Progress in Human Development In...
 CareEdge State Rankings 2025: Maharashtr...
CareEdge State Rankings 2025: Maharashtr...
 Top 10 Most Expensive Cities To Live Aro...
Top 10 Most Expensive Cities To Live Aro...








