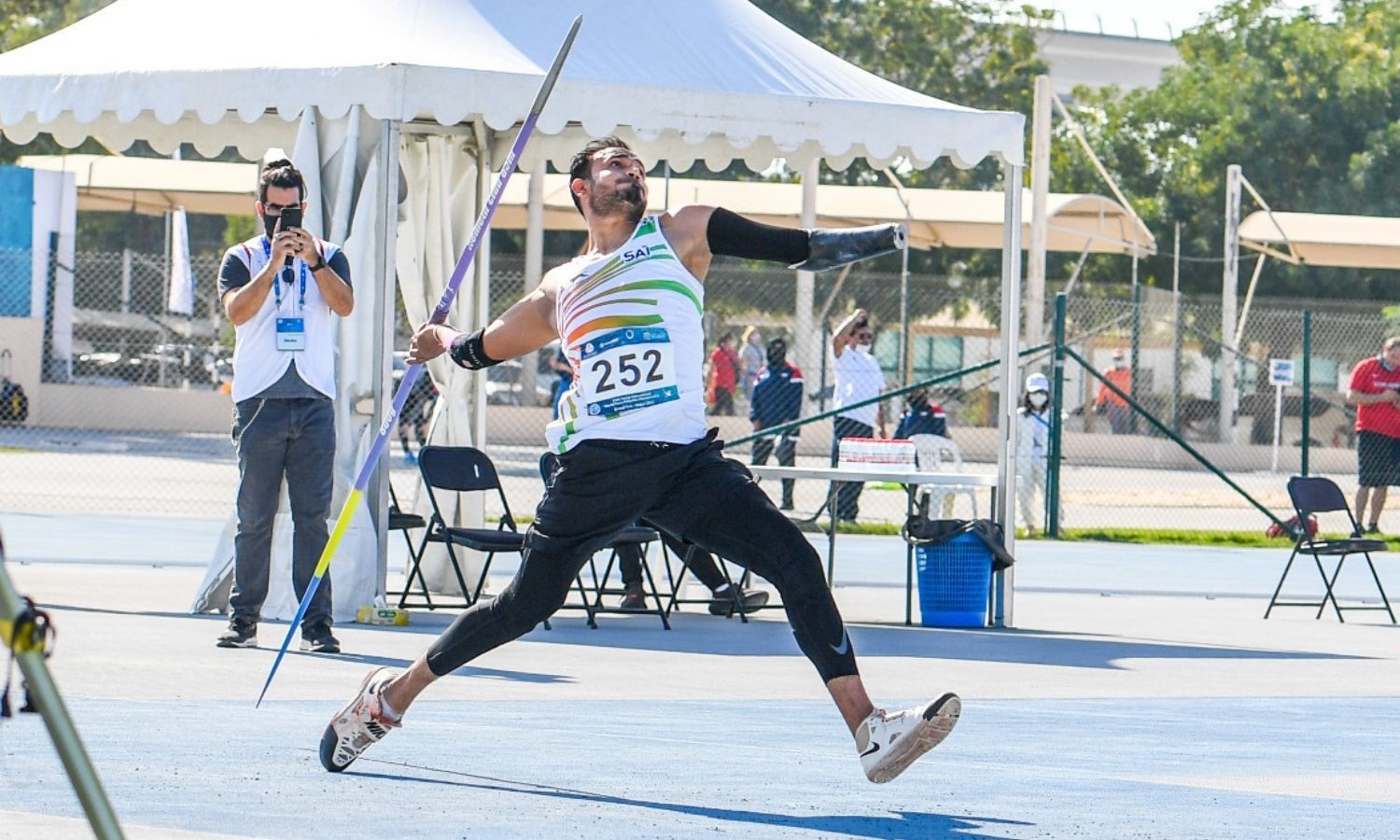
The Charlety Stadium in Paris hosted the Para Athletics World Championships from 8 to 17 July, attracting a diverse participation of more than 1200 athletes from 107 nations. Ajeet Singh displayed his exceptional prowess in the finals of the Men’s javelin throw F46 category, emerging as the champion and claiming the gold medal. With a remarkable throw measuring 65.41 meters, he secured the top spot in the competition. Ajeet Singh’s outstanding performance not only earned him the championship title but also resulted in the breaking of the previous record held by Chunliang Guo of China, whose throw measured 61.89 meters.
Indian Athletes at the 2023 World Para Athletics Championships in Paris
India concluded its participation in the 2023 World Para Athletics Championships held in Paris with an exceptional achievement, breaking records and securing an impressive medal count. They garnered three gold medals, four silver medals, and three bronze medals, setting a new benchmark.
In the Men’s Javelin Throw F64 category, Sumit Antil clinched India’s first gold medal. Notably, he surpassed his own World Record with a remarkable throw of 70.83 meters, earning him a coveted spot in the 2024 Paris Paralympic Games. Adding to India’s triumph, Sachin Sarjerao Khilari secured the second gold medal in the Men’s Shot Put F46 category, also securing his place in the 2024 Paris Paralympics.
Completing India’s gold medal haul, Ajeet Singh triumphed in the Men’s Javelin Throw F46 Final. Sunder Singh Gurjar showcased an impressive performance as well, finishing fourth in the same event and securing qualification for the 2024 Paris Paralympics.
This outstanding performance by the Indian contingent marks their best-ever achievement in the competition, surpassing their previous record of nine medals in the 2019 edition held in Dubai.
Key takeaways for competitive examinations
- Ajeet Singh hails from: Uttar Pradesh, India
- Total medal won by India in the 2023 World Para Athletics Championships: 10