
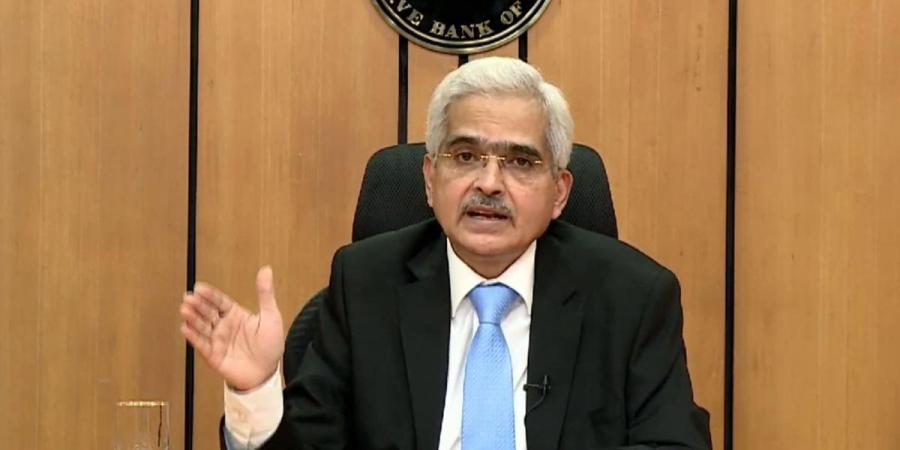
The six-member Monetary Policy Committee of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), headed by Governor Shaktikanta Das, has decided to maintain the status quo on policy rate amid sticky rate of inflation. At this point, the repo rate or the rate at which RBI lends to banks stands unchanged at 4 per cent. The reverse repo rate also stayed unchanged at 3.35 per cent. The MPC committee members voted unanimously in favour of the decision.
The key decisions taken in the Monetary Policy Committee meeting are:
- Policy Repo Rate: 4.00%
- Reverse Repo Rate: 3.35%
- Marginal Standing Facility Rate: 4.25%
- Bank Rate: 4.25%
- CRR: 3%
- SLR: 18.00%
RBI Monetary Policy Highlights & Key Decisions:
- The MPC continued to maintain the accommodative stance.
- The MPC has predicted the economic growth rate i.e. GDP growth rate of India at 10.5 per cent in 2021-22 (FY22).
- This is the first MPC meeting after the presentation of the Union Budget 2021-22.
- The six-member MPC headed by RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das meets every two months to analyze the state of the Indian economy and inflation and address the monetary issues in the country.
WARRIOR 5.0 Batch for SBI, RRB, RBI and IBPS Exams Banking Awareness Online Coaching | Bilingual
The composition of the Monetary Policy Committee is as follows:
- Governor of the Reserve Bank of India – Chairperson, ex officio: Shri Shaktikanta Das.
- Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, in charge of Monetary Policy– Member, ex officio: Dr Michael Debabrata Patra.
- One officer of the Reserve Bank of India to be nominated by the Central Board – Member, ex officio: Dr Mridul K. Saggar.
- A professor at the Mumbai-based Indira Gandhi Institute of Developmental Research: Prof. Ashima Goyal.
- A professor of finance at the Indian Institute of Management in Ahmedabad: Prof. Jayanth R Varma.
- An agricultural economist and a senior adviser with the National Council of Applied Economic Research in New Delhi: Dr Shashanka Bhide.
Some important instruments of Monetary Policy:
The RBI’s Monetary Policy has several direct and indirect instruments which are used for implementing the monetary policy. Some important instruments of Monetary Policy are as follows:
Repo Rate: It is the (fixed) interest rate at which banks can borrow overnight liquidity from the Reserve Bank of India against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
Reverse Repo Rate: It is the (fixed) interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India can absorb liquidity from banks on an overnight basis, against the collateral of eligible government securities under the LAF.
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF): The LAF has overnight as well as term repo auctions under it. The term repo helps in the development of the inter-bank term money market. This market sets the benchmarks for pricing of loans and deposits. This helps in improving the transmission of monetary policy. As per the evolving market conditions, the Reserve Bank of India also conducts variable interest rate reverse repo auctions.
Marginal Standing Facility (MSF): MSF is a provision which enables the scheduled commercial banks to borrow an additional amount of overnight money from the Reserve Bank of India. Bank can do this by dipping into their Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) portfolio up to a limit at a penal rate of interest. This helps the banks to sustain the unanticipated liquidity shocks faced by them.
Important takeaways for all competitive exams:
- RBI 25th Governor: Shaktikant Das; Headquarters: Mumbai; Founded: 1 April 1935, Kolkata.
Find More News on Economy Here




 States and Capitals of India, Check the ...
States and Capitals of India, Check the ...
 Which is the Largest District of Maharas...
Which is the Largest District of Maharas...
 Which is the Biggest Mall in Hyderabad? ...
Which is the Biggest Mall in Hyderabad? ...

