Context:
According to the study, an infectious bacterium, Fusobacterium is linked with endometriosis in some women. Scientists are yet to figure out why the locations of the lesions vary in each woman.
Endometriosis:
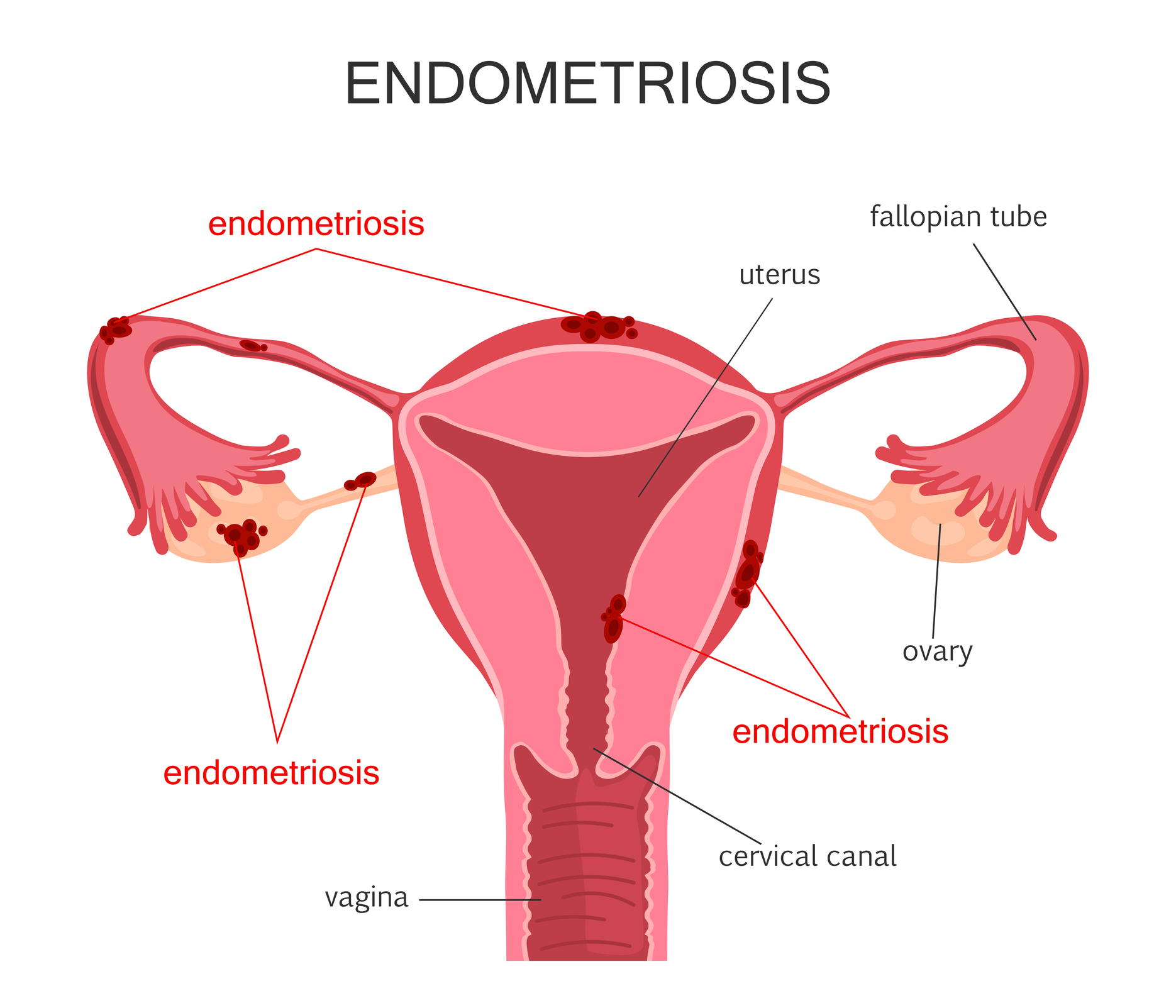
Endometriosis is a disease in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. It can cause severe pain in the pelvis and make it harder to get pregnant.
Endometriosis can start at a person’s first menstrual period and lasts until menopause.
Endometriosis is a reproductive disease which affects one in ten women.
Common causes
One of the common causes of endometriosis can be retrograde mensuration– when some part of the menstrual disease flows backward into the abdominal region instead of flowing out of the vagina that can cause endometriosis.
The inability of the immune system to detect and eliminate blood cells from retrograde mensuration, allowing it to persist in the pelvic region, points to some dysfunction in the immune system.
Fusobacterium:
Fusobacterium has links to infections of the gum, vagina and rectum-yet it isn’t commonly found in meaningful quantities in the gut.
Experts have suggested that it could be moving to the abdomen through the bloodstream or to the vaginal region from the rectum.
What do the findings say?
There are only few treatment options are available even after the diagnosis of an average of six years.
According to the study, fibrous food can help to manage the conditions because while metabolites released by certain microbes aggravate endometrial lesions, other metabolites produced by the fermentation of certain types of food can protect from the condition. This is because the latter can decrease the abundance of Fusobacterium and other infectious bacterial species. Find More Miscellaneous News Here



 Which Place is known as the Diamond Capi...
Which Place is known as the Diamond Capi...
 List of Major LPG Gas Companies in India...
List of Major LPG Gas Companies in India...
 WHO Foundation and Novo Nordisk Launch I...
WHO Foundation and Novo Nordisk Launch I...








