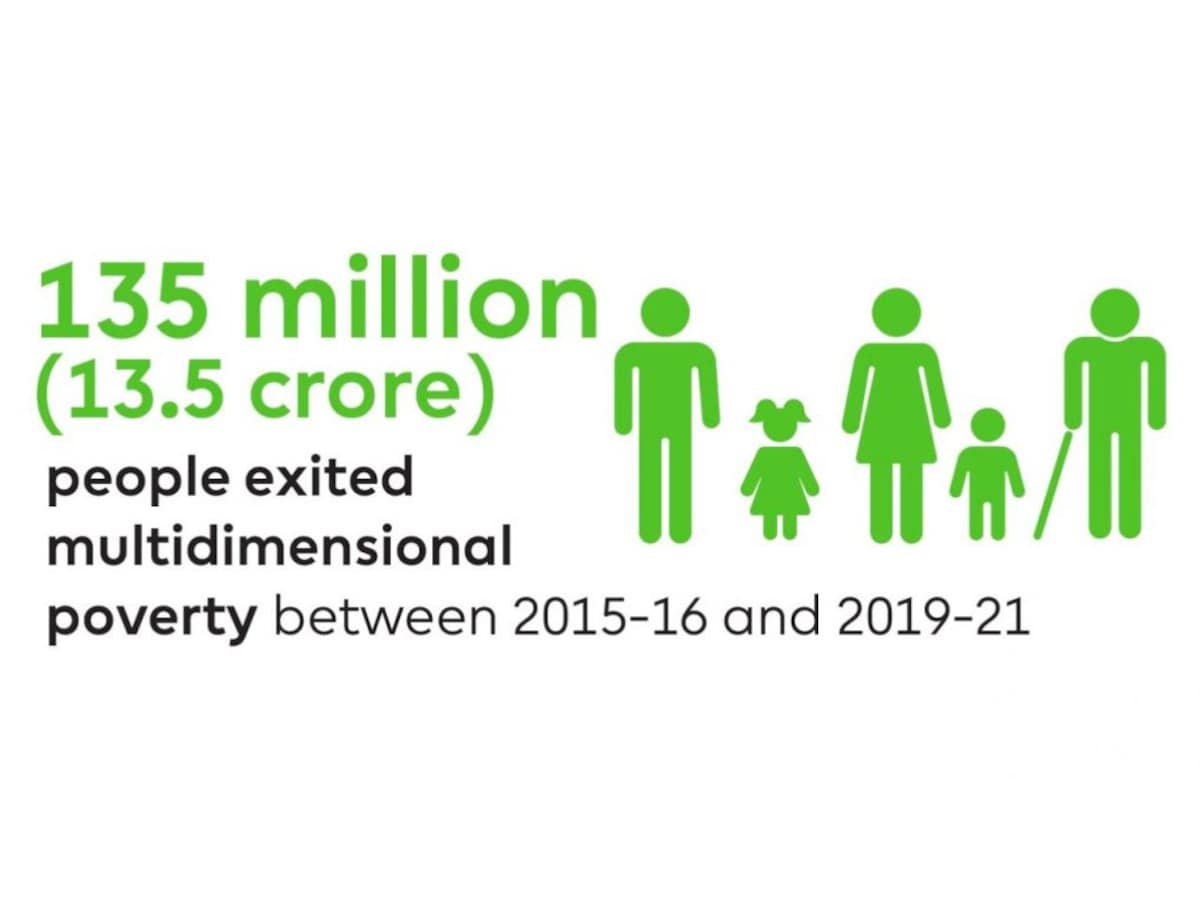
According to the latest NITI Aayog report, India has achieved a remarkable feat in its efforts to reduce multidimensional poverty. Between 2015-16 and 2019-21, a staggering 13.5 crore people moved out of multidimensional poverty, showcasing the country’s commitment to sustainable and equitable development.
Comprehensive Methodology and Progress
The report, ‘National Multidimensional Poverty Index: A Progress Review 2023,’ draws its data from the latest National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) conducted between 2019 and 2021. It builds upon the baseline report launched in 2021 and follows a methodology aligned with global standards. The National MPI measures deprivations in health, education, and standard of living through 12 SDG-aligned indicators.
Striking Improvements Across Indicators
India has witnessed marked improvements in all 12 indicators, including nutrition, child and adolescent mortality, maternal health, education, sanitation, and access to basic amenities like drinking water and electricity. The results indicate a decline of 9.89 percentage points in the number of multidimensionally poor, reducing from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-2021.
Rural Areas Leading the Way
The report highlights that the decline in multidimensional poverty was most prominent in rural areas, decreasing from 32.59% to 19.28%. Urban areas also witnessed a reduction, going from 8.65% to 5.27%. Uttar Pradesh showed significant progress, with 3.43 crore people escaping multidimensional poverty, marking the largest decline among all states.
Path Towards SDG 2030
India’s progress is commendable as the MPI value has nearly halved from 0.117 to 0.066, and the intensity of poverty has reduced from 47% to 44%. This puts India well on track to achieve SDG Target 1.2 of reducing multidimensional poverty by at least half much ahead of the 2030 timeline. The government’s strategic focus on inclusive development and poverty eradication has played a pivotal role in this achievement.
Government Initiatives Driving Change
Flagship programs like Poshan Abhiyan, Anaemia Mukt Bharat, Swachh Bharat Mission, Jal Jeevan Mission, Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana, PMAY, PMJDY, and Samagra Shiksha have significantly contributed to improving access to healthcare, sanitation, nutrition, cooking fuel, financial inclusion, housing, and education. The efforts have resulted in reduced deprivations across various indicators, showcasing the impact of consistent implementation of well-linked initiatives.




 Weekly Current Affairs One Liners 16th t...
Weekly Current Affairs One Liners 16th t...
 Which District is known as the Medical C...
Which District is known as the Medical C...
 Which was the First Women's University i...
Which was the First Women's University i...








