Chandrayaan-3, building upon Chandrayaan-2, aims to demonstrate advanced lunar exploration capabilities. Consisting of a Lander and Rover configuration, this mission endeavors to uncover the Moon’s secrets through scientific payloads and cutting-edge technology.
Lander Module:
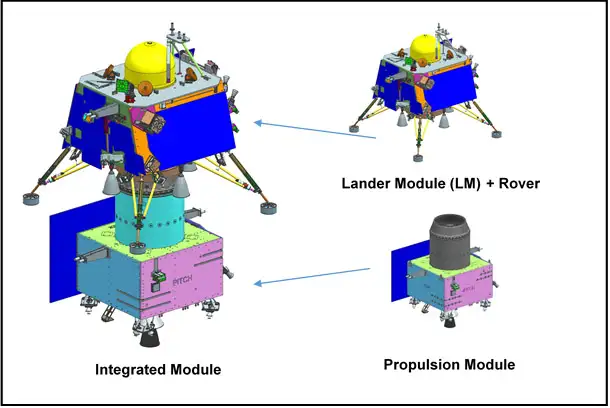
- The indigenous Lander module is the centerpiece of Chandrayaan-3.
- Designed for soft landing, it carries scientific payloads to study lunar phenomena.
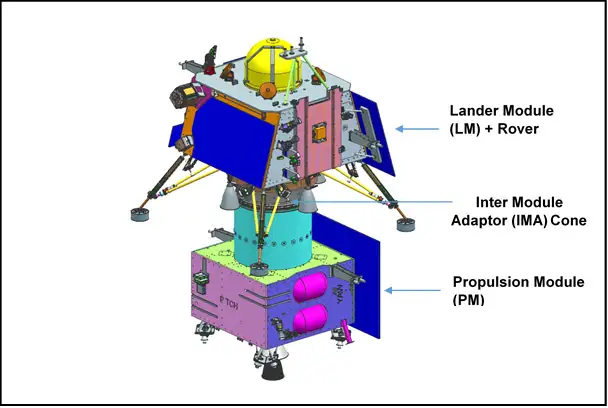
- Propulsion Module (PM) carries the Lander and Rover configuration to a 100 km lunar orbit.
- PM features the Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload, analyzing Earth’s spectral and polarimetric measurements from lunar orbit.
Lander Payloads:
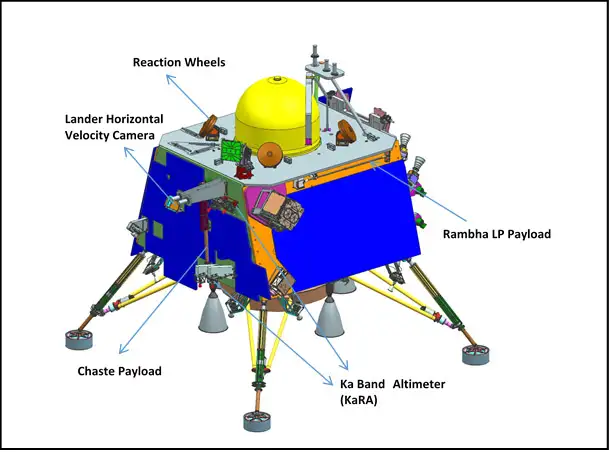
- Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE): Measures thermal conductivity and temperature.
- Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA): Gauges seismicity around the landing site, probing lunar crust and mantle.
- Langmuir Probe (LP): Estimates plasma density and variations.
- Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA): NASA’s passive experiment for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover Payloads:
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS): Derives elemental composition of lunar soil and rocks.
- Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS): Provides insights into chemical and mineral composition near the landing site.
Advanced Technologies and Objectives:
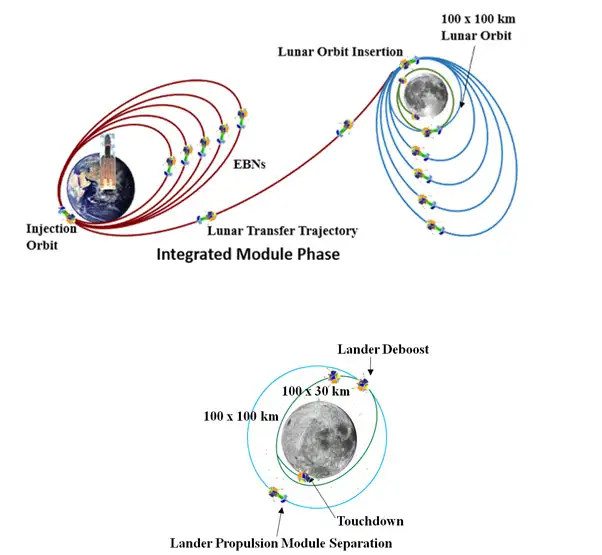
- Chandrayaan-3 aims to demonstrate advanced technologies for interplanetary missions.
- Lander employs altimeters, velocimeters, inertial measurement, propulsion systems, navigation, and hazard detection for safe landing.
- Mission objectives encompass safe landing, rover mobility, and in-situ scientific experiments.
Mission Specifications:
- Chandrayaan-3’s mass is 3900 kg, with Propulsion Module at 2148 kg and Lander Module at 1752 kg.
- Power generation ranges from 50W (Rover) to 758W (Propulsion Module).
- Communication involves IDSN links for Propulsion Module and Lander, with contingency link to Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter.
Scientific Payloads Significance:
- Lander payloads study lunar plasma, thermal properties, seismic activity, and cosmic dynamics.
- Rover payloads unravel elemental and mineral composition, enriching lunar geological knowledge.
- Chandrayaan-3 contributes to exploring lunar history, Solar System evolution, and potential for future lunar bases.




 What is the Strait of Hormuz? Know About...
What is the Strait of Hormuz? Know About...
 Which Country is the Largest Consumer of...
Which Country is the Largest Consumer of...
 Amol Palekar to Receive META Lifetime Ac...
Amol Palekar to Receive META Lifetime Ac...








