Monkeypox Virus
Another virus, Monkeypox, has made an appearance in the United Kingdom. The patient has a recent travel history from Nigeria, where they are suspected to have contracted the infection, before travelling to the UK, according to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), which confirmed the case.
21-day quarantine compulsory for monkeypox patients
What is Monkeypox Virus?
- Monkeypox is a viral disease caused by the Monkeypox virus, which belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family and is associated with diseases such as smallpox, cowpox, horsepox, and camelpox.
- Monkeypox has symptoms that are comparable to smallpox, which was proclaimed eradicated in the 1980s.
- It was first discovered in humans in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970, two years after smallpox had been eradicated from the area.
- According to WHO records, the majority of Monkeypox cases have been reported from rural, rainforest regions of the Congo Basin since 1970, mainly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it is currently considered endemic.
Monkeypox Virus History:
- According to a scientific report, the Monkeypox virus was initially discovered in a colony of Cynomolgus monkeys kept at the State Serum Institute in Copenhagen in 1958. “Monkeypox was first introduced into the Rotterdam Zoo in 1966.
- The disease first struck giant anteaters from South America, but it quickly spread to other ape and monkey species.
- The viruses obtained from these animals were discovered to be identical and to constitute an orthopoxvirus species not previously characterised.
- The Congo Basin and West African clades of the Monkeypox virus are responsible for the disease. Clades are collections of creatures that have a common ancestor. Coronavirus, for example, is a clade within the coronaviridae family.
- The Congo Basin clade of Monkeypox virus is the more virulent and transmissible of the two genetic clades.
About Monkeypox Virus Outbreak:
- According to the WHO, the first large Monkeypox outbreak was detected in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1996–97, with lower case fatality and a greater attack rate.
- A Monkeypox epidemic was detected in the United States in 2003, marking the first time the disease had been reported outside of Africa. “In 2003, 47 cases of Monkeypox were confirmed or suspected in six states: Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Missouri, Ohio, and Wisconsin.
- All Monkeypox patients in this outbreak became ill after coming into contact with pet prairie dogs.
- After being housed near imported small mammals from Ghana, the pets became ill. Human monkeypox had never been recorded outside of Africa before “the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States
- In 2017, Nigeria saw the largest documented outbreak in 40 years.
- Travellers from Nigeria who became ill with Monkeypox after arriving in Israel in September 2018, the United Kingdom in September 2018 and December 2019, and Singapore in May 2019 carried the disease.
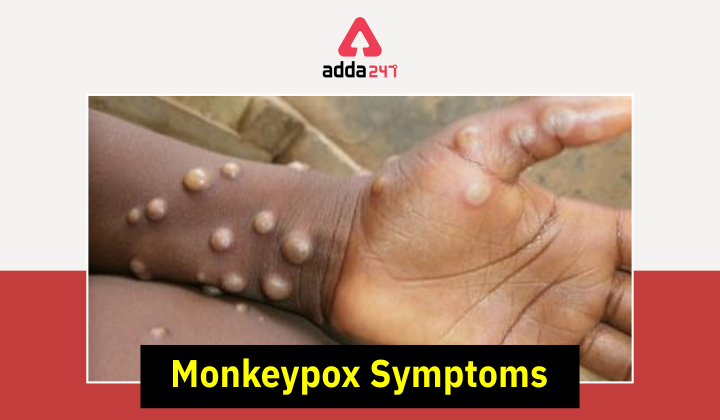
Symptoms of monkeypox:
- During a Monkeypox viral attack, the symptoms can be divided into two categories: invasion and skin rash.
- Monkeypox typically takes 6 to 13 days to incubate.
- The incubation period is the time between when an infection occurs and when symptoms develop in a person.
- The patient has fever, acute headache, lymphadenopathy (swelling of the lymph nodes), back pain, myalgia (muscle aches), and an intense asthenia during the invasion stage, which is within the first 5 days of the illness (lack of energy).
The patient will develop skin rashes 1-3 days after the fever, with the rash being centred on the face and extremities rather than the trunk. The patient will get skin rashes 1-3 days after the fever has passed. “The rash appears to be localised more on the face and extremities than on the trunk. The face (in 95% of cases), palms of the hands, and soles of the feet are all affected (in 75 percent of cases). Oral mucous membranes (70 percent of cases), genitalia (30 percent), and conjunctivae (20 percent) are also affected as well as cornea, according to a WHO report.
Buy Prime Test Series for all Banking, SSC, Insurance & other exams



 States and Capitals - How Many States in...
States and Capitals - How Many States in...
 Anil Nagar, Founder & CEO of Adda Ed...
Anil Nagar, Founder & CEO of Adda Ed...
 Top-10 Smallest Districts of Uttar Prade...
Top-10 Smallest Districts of Uttar Prade...

